Complex curves are comprised of an X data vector and a Y and Y2 data vector. The X and Y vectors can be read from a data file, defined as mathematical expressions, or entered as values. The X and Y vectors of a curve do not have to come from the same source. For instance, the data source for the X vector of a curve can be an ASCII file and the source for the Y vector of the same curve can be defined by an expression such as sqrt(x).
If File is selected as the source, the file panel is displayed, allowing you to select data files for the X, Y, and Y2 vectors.
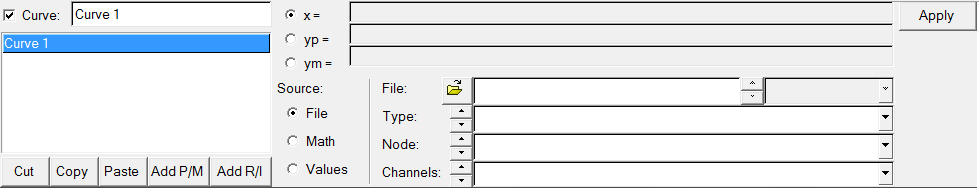
File selected as the data source for a vector.
|
If Math is selected as the source, the curve calculator is displayed, allowing you to define the vector mathematically.
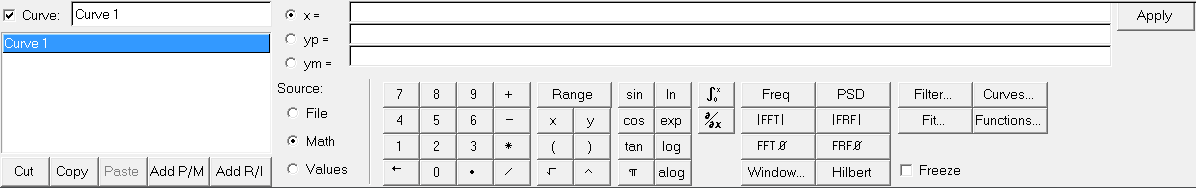
Math selected as the data source for a vector.
| Note | See Curve Calculator for more information on defining vectors mathematically and signal processing. |
|
If Values is selected as the source, the Values table is displayed, allowing you to directly enter data point values.
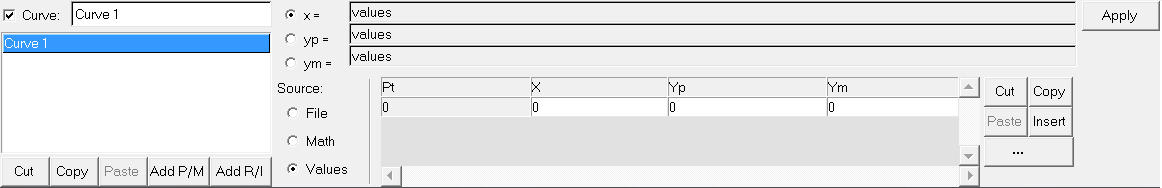
Value selected as the data source for a vector.
You can cut, copy, paste, and insert data point values to the table. Click the expansion button,  , to view a larger dialog containing all X, Y, and Y2 data points. , to view a larger dialog containing all X, Y, and Y2 data points.
|
How do I...
| 1. | From the Define Curves panel, select Values. |
| 2. | Select a point from the table. |
The data points are added to the next row in the table.
|
| 1. | From the Define Curves panel, select Values. |
| 2. | Select a point from the table. |
The X, Y, and Y2 data points are removed from the table.
|
| 1. | Select a curve from the list or pick a curve from the window. |
| 2. | Click on the corresponding vector radio button to edit the X, Y, or Y2 data vector. |
| 3. | Select or enter the new data for the vector. |
The changes to the curve are reflected in the HyperGraph 2D window.
|
| 1. | From the Define Curves panel, select Values. |
| 2. | Select a point from the table. |
A new row is added above the selected row. The X, Y, and Y2 data values are all zero by default, allowing you to enter new values.
|
| 2. | Click the file browser button and select a data file. |
| 3. | Click on the X vector radio button. |
| 4. | Select an X vector data source from Subcase. |
| 5. | Click the Y vector radio button. |
| 6. | Select a Y vector data source from Subcase. |
| 7. | Click the Y2 vector radio button. |
| 8. | Select a Y2 vector data source from Subcase. |
|
| 2. | Define the vector using the curve calculator to create a mathematical expression. |
|
| 1. | From the Define Curves panel, select Values. |
| 2. | Select Pha/Mag or Real/Img. |
| 3. | Enter X, Y, and Y2 values in the Values table. |
|







