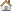This tutorial demonstrates how to perform an optimization study for an application where only design data in a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet is available (i.e.: no simulation model exists). The Excel spreadsheet study.xls used in this tutorial can be found in <hst.zip>/HS-2200/ and copied to your working directory.
The objective of this tutorial is to create a fit (approximation) using the designs in the spreadsheet and then to perform an optimization study using the fit.
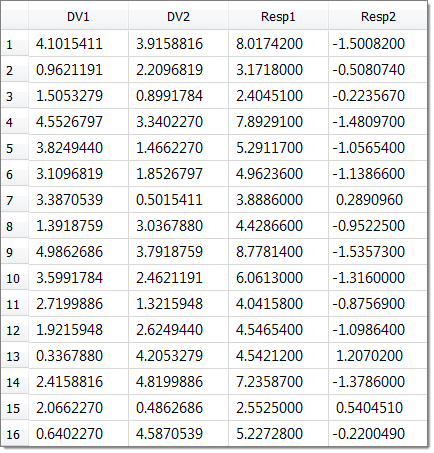
The spreadsheet used here contains five columns. The first column contains the numbering of the designs, the second and third columns contain the values of the two input variables for each design, and the fourth and the fifth columns contain the results of a DOE study previously run. Sixteen designs have been evaluated.
| 2. | To start a new study, click File > New from the menu bar, or click  on the toolbar. on the toolbar. |
| 3. | In the HyperStudy – Add dialog, enter a study name, select a location for the study, and click OK. |
| 4. | Go to the Define models step. |
| 5. | Add an Internal Math model. |
| b. | In the HyperStudy - Add dialog, add one Internal Math model. |
| 6. | Go to the Define Input Variables step. |
| 7. | Click Add Input Variable. |
| 8. | In the HyperStudy - Add dialog, add two input variables. |
| 9. | Optional. Copy the input variable labels from the study.xls spreadsheet, and paste them into the Labels column of the work area. |
| Note: | When you paste the input variable labels into the work area, select Paste transpose from the context menu. |
| 10. | Go to the Specifications step. |
|
| 1. | In the work area, set the Mode to Nominal Run. |
| 3. | Go to the Evaluate step. |
| 5. | Go to the Define Output Responses step. |
|
| 1. | Click Add Output Response. |
| 2. | In the HyperStudy - Add dialog, add two output responses. |
| 3. | Optional. Copy the output response labels from the study.xls spreadsheet, and paste them into the Label column in the work area. |
| Note: | When you paste the input variable labels into the work area, select Paste transpose from the context menu. |
| 4. | Go to the Post processing step. |
|
| 1. | In the Explorer, right-click and select Add Approach from the context menu. |
| 2. | In the HyperStudy - Add dialog, select Doe and click OK. |
| 3. | Go to the Specifications step. |
| 4. | In the work area, set the Mode to None. |
| 6. | In the top, right of the work area, select Edit > Run Matrix. |
| 7. | In the Run Matrix dialog, click Add Run to add 16 runs to the matrix, as there are 16 runs in the study.xls spreadsheet. |
| 8. | Open the study.xls spreadsheet in Excel. |
| 9. | Copy all of the input variable and output response data for each run in the spreadsheet. |
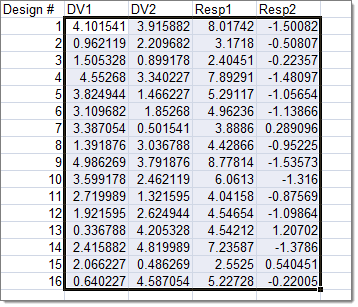
| 10. | In the Run Matrix dialog, highlight all of the runs in the matrix. |
| 11. | Right-click on the highlighted runs, and select Paste from the context menu. HyperStudy pastes the input variable and output response data that you copied from the study.xls spreadsheet into the run matrix. |
|
| 1. | In the Explorer, right-click and select Add Approach from the context menu. |
| 1. | In the HyperStudy - Add dialog, select Fit and click OK. |
| 2. | Go to the Select matrices step. |
| 4. | In the HyperStudy - Add dialog, add one matrix. |
| 6. | Go to the Specifications step. |
| 7. | In the work area, set the Mode to Moving Least Squares (MLSM). |
| 8. | In the Settings tab, change the Order to 3 + interactions. |
| 10. | Go to the Evaluate step. |
| 12. | Go to the Post processing step. |
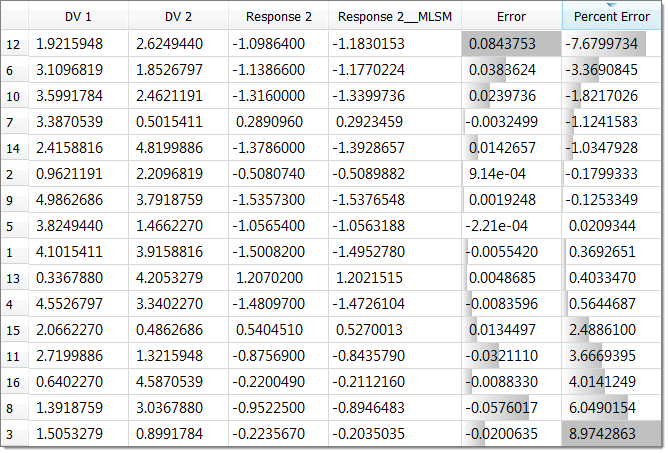
| 13. | Click the Residuals tab to investigate the accuracy of your approximation. From the table you can see that this approximation is not as good. |
|
See Also:
HyperStudy Tutorials