Radial Basis Function |

|

|

|

|
|
Radial Basis Function |

|

|

|

|
Radial basis function method is a Fit method that uses linear combinations of basis functions. Typical basis functions are linear, cubic, thin-plate spline, Gaussian, multiquadric, and inverse-multiquadric. These basis functions are observed to be accurate for highly nonlinear output responses but not for linear output responses. To remedy this deficiency, in HyperStudy, a RBF model is augmented with a polynomial function:
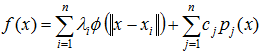
where ![]() is the number of sampling points,
is the number of sampling points, ![]() is a vector of input variables,
is a vector of input variables, ![]() is the
is the ![]() sampling point,
sampling point, ![]() is the Euclidean norm,
is the Euclidean norm, ![]() is a basis function, and
is a basis function, and ![]() is the coefficient for the
is the coefficient for the ![]() basis function.
basis function. ![]() is a low-order (constant or linear) polynomial function;
is a low-order (constant or linear) polynomial function; ![]() is the total number of terms in the polynomial, and
is the total number of terms in the polynomial, and ![]() are the unknown coefficients.
are the unknown coefficients.
| • | RBF tries to go through the exact sampling points, and in general, the residuals are small, if not zero. As a result, diagnostic measures using only the complete input matrix do not produce meaningful values. Cross-validation results provide some diagnostics using a special scheme using only the input points. To get detailed diagnostics on the quality of a RBF fit, it is suggested that you use a validation matrix. |
| • | Suitable for modeling highly nonlinear output response data that does not contain numerical noise. |
| • | Applicability of HyperKriging and Radial Basis Function (RBF) methods are similar in terms of physics (they both are suggested for highly nonlinear output responses with no noise). It is suggested that you use HyperKriging for large studies that contain a large number of sampling points, whereas, RBF is suggested for studies with a large number of variables. |
| Note: | As a result, RBF Fits are evaluated faster than HyperKriging Fits when used in approaches. |
In the Specifications step, you can change the the following RBF settings from the Settings tab.
|
Parameter |
Default |
Range |
Description |
Augmented Function |
Constant |
Constant or Linear |
Type of augmented function. |
Maximum Points |
2000 |
>= 100 |
The maximum number of points for building RBF; if number of building points is larger than maxnpt, then the point reduction algorithm is activated and a warning message is shown; the purpose of introducing maxnpt is to reduce computational effort for large scale problems. |
RBF Type |
CS21 |
Multiquadric CS21 (formally knows as Wu's Compactly Supported (2,1)) Gaussian |
Type of RBF. |
Relaxation Parameter |
1.0 |
>= 0.0 |
Relaxation parameter d used in RBF; if RBF is CS21 or Gaussian, and d is set to 0.0 by users, then RBF will automatically set d = 1.0e-6. |