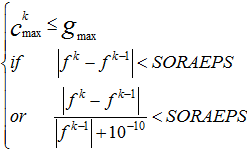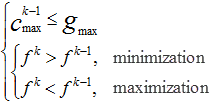Sequential Optimization and Reliability Assessment (SORA), originally published by Dr. W. Chen and Dr. X. Du of Northwestern University, is a reliability-based design optimization method. Reliability-based design optimization (RBDO) methods take uncertainties in the design into account and search for designs that satisfy the design requirements with a required probability of success. A reliability-based design problem is formulated as follows:
Objective:
|
min f(x, r, p)
|
Constraints:
|
P(g(x,r, p ≤ 0.0) > PS
|
where,
x is the deterministic input variables.
r is the random input variables (affect the design but are subject to uncertainties).
p is the pure random parameters (variables we have no control over but affect the design, such as humidity and temperature).
Usability Characteristics
| • | An extension of SORA is implemented in HyperStudy to allow for robust design optimization. Robust design optimization attempts to minimize the objective variance in order to reduce its sensitivity to design variations and consequently increase the design's robustness. The implementation in HyperStudy is based on the use of percentiles for the objective function and is turned on via the Robust Optimization setting in the Specification step. |
| • | SORA is the most accurate of the three RBDO methods available in HyperStudy. It is also the most expensive. |
| • | SORA terminates if one of the conditions below are met: |
| - | One of the two convergence criterias are met. |
| o | The absolute objective change is less than a convergence tolerance value (SOREPS) and there is no constraint violation (GMAX). |
| o | The relative objective change is less than a convergence tolerance value (SOREPS) and there is no constraint violation (GMAX) in the last design. |
| - | The maximum number of allowable iterations (MAXDES) is reached. |
An exception is when the current objective is worse than the previous objective and the constraint violation of the previous design is within allowable violation. When this occurs, SORA will be terminated.
| • | The reliability analysis is carried out by searching for the most probable point (MPP). Issues such as non-uniqueness of the MPP and highly non-linear output response functions can reduce the accuracy of the reliability calculation. |
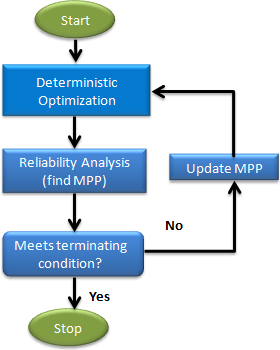
The flowchart below illustrates the different phases of the SORA process.
Settings
In the Specifications step, you can change the settings of SORA from the following tabs:
In the Settings tab, you can access the settings listed below. Please note that for most applications the default settings work optimally, and you may only need to change the Maximum Iterations and Robust Optimization.
Setting
|
Default
|
Range
|
Description
|
Maximum Iterations
(MAXDES)
|
25
|
> 0
|
Maximum number of iterations allowed.
|
Robust Optimization
(ROBUST)
|
0
|
0, 1
|
To decide whether this is a robust optimization or not; 0 means that you do not use robust optimization; 1 means that robust optimization is used.
|
Constraint violation tol.
(GMAX)
|
0.1
|
> 0.0
|
Global maximum allowable percentage constraint violation. Constraints must not be violated by more than this value in the converged design.
|
Robust Min %
(ROBMINPV)
|
95.0
|
>50,
<100
|
Define percentile value of robust optimization for minimization objective.
|
Robust Max %
(ROBMAXPV)
|
5.0
|
>0,
<50
|
Define percentile value of robust optimization for maximization objective.
|
|
In the More tab, you can access the setting listed below. Please note that for most applications, the default settings work optimally.
Setting
|
Default
|
Range
|
Description
|
Angle convergence tol.
(MPPTOL)
|
0.25
|
>0.0
|
Angle convergence tolerance for inverse MPP search, in unit of degrees. If the angle between the vector of 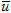 (design point in standard normal distribution space) and the negative gradient falls within the tolerance, then inverse MPP search is regarded as converged. (design point in standard normal distribution space) and the negative gradient falls within the tolerance, then inverse MPP search is regarded as converged.
A smaller value favors a higher precision of reliability analysis, but more computational effort is needed.
|
Termination criteria
(SOREPS)
|
1.0E-4
|
>0.0
|
Termination tolerance.
If the absolute or relative change of the objective value is less than this value, and the constraint violation is not larger than this value, then SORA will be terminated. There also must not be any constraint with an allowable violation that has been exceeded in the last design.
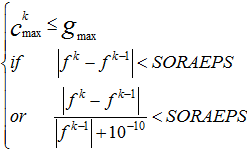
Where, 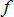 is the objective; is the objective; 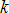 is the current iteration number; is the current iteration number; 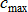 is the maximum constraint violation; is the maximum constraint violation; 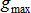 is the allowable constraint violation; SOREPS is the value of the termination criteria. is the allowable constraint violation; SOREPS is the value of the termination criteria.
An exception is when the current objective is worse than the previous objective and the constraint violation of the previous design is within allowable violation, SORA will be terminated.
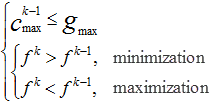
|
Constraint threshold
(EPSCON)
|
1.0e-4
|
> 0.0
|
This parameter is used for constraint value calculation. In general, constraint value is normalized to its bound value. One exception is that constraint value is not normalized if its absolute bound value is less than this parameter. Recommended range is 1.0e-6 ~ 1.0.
|
|