Definition
Skews and frames are used to define local directions. These directions can be used to apply:
To define:
| • | rigid body added inertia frame |
| • | general spring reference frame |
| • | beam type spring initial reference frame |
| • | nodal time history output frame |
Two reference definitions are available in RADIOSS:
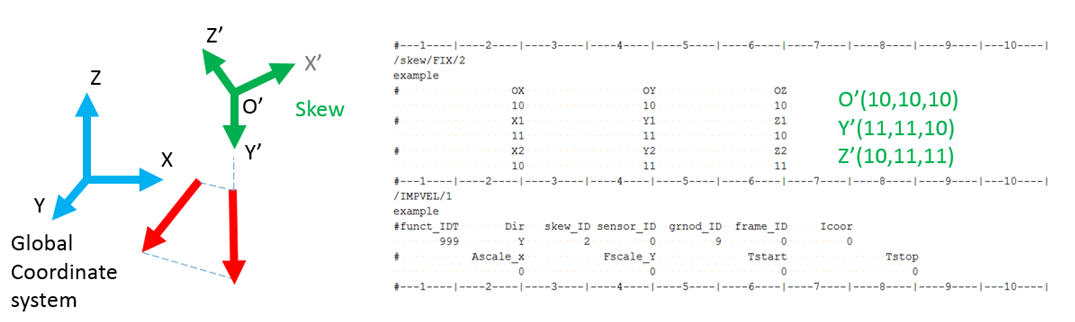
It is a projection reference to define the local quantities with respect to the global reference. In fact, the origin of the skew remains at the initial position during the motion even though a moving skew is defined. In this case, a simple projection matrix is used to compute the kinematic quantities in the reference.
In this example imposed velocity is applied in Y direction. In /IMPVEL skew is used, then the imposed velocity is computed in the Y-axis of global coordinate system and then projected onto the Y’ axis of local skew reference.
|
It is a mobile or fixed reference. The quantities are computed with respect to the origin of the frame which may be in motion or not depending on the kind of reference frame. For a moving reference frame, the position and the orientation of the reference vary in time during the motion. The origin of the frame defined by a node position is tied to the node.
Frame measures relative motion whereas skew measures global motion and projects it to skew. Only few options use frame like imposed velocity, TH/NODE and others use skew.
In this example rotational velocity is applied around Z axis. In /LOAD/CENTRI frame is used, then rotational velocity is around Z’ axis of frame reference not in Z axis of global coordinate system anymore.

|







