In this tutorial, you will:
| • | Delete untrimmed surfaces |
| • | Set the cleanup tolerance |
| • | Delete duplicate surfaces |
The benefits of importing and repairing CAD are:
| • | Correcting any errors in the geometry from import |
| • | Creating the simplified part needed for the analysis |
| • | Meshing a part all at once |
| • | Ensuring proper connectivity of mesh |
| • | Obtaining a desirable mesh pattern and quality |
Model Files
This exercise uses the clip_repair.hm file, which can be found in the hm.zip file. Copy the file(s) from this directory to your working directory.
Exercise: Importing and Repairing CAD Geometry Data
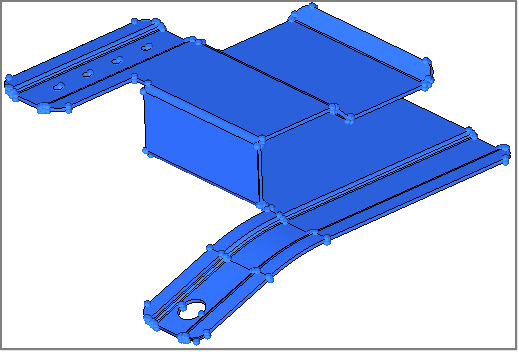
Step 1: Open and view the model file, clip_repair.hm.
| 1. | Start HyperMesh Desktop. |
| 2. | From the menu bar, click File > Open > Model. |
| 3. | In the Open Model dialog, open the clip_repair.hm model file. |
Step 2: View the model in topology display toolbar and shaded mode to evaluate its integrity.
| 1. | Observe where the model has incorrect connectivity and missing or duplicate surfaces. |
| 2. | To open the Auto Geometry Cleanup panel, click Geometry > Autocleanup from the menu bar. The surface edges are now colored according to their topology status. |
| Note: | This occurs because Geometry Color is set to  . . |
| 3. | To display the model's geometry in wire frame mode, click  on the Visualization toolbar. on the Visualization toolbar. |
| Note: | The Visualization toolbar contains icons that control the display of the surfaces and surface edges. Surfaces can be shaded with or without edges or wireframe. Right-click the icons to access the drop-down menu for additional options. Place your mouse over the cursor to view a description of the button’s functionality. |
| 4. | To open the Visualization browser and access the Topology options, click  . . |
| Note: | The Topology options control the display of the surfaces and surface edges. Surfaces can be shaded or wireframe. The check boxes within the Visualization browser turn the display of the different edge types and fixed points (surface vertices) on or off. |
| 5. | Select only the Free check box. The graphics area displays only the free edges. |
| 6. | Observe the free (red) edges and make note of where they are. Free edges show where there is incorrect connectivity or gaps. |
| 7. | Observe the locations where there are closed loops of free edges. These are locations that probably have missing surfaces. |
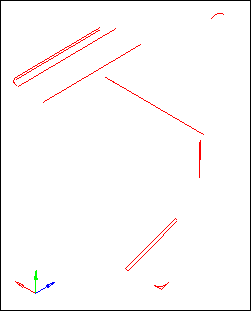
Free edges indicating surface discontinuities of the clip geometry
| 8. | Select only the Non-manifold check box. |
| 9. | Observe the non-manifold edges and make note of where they are. Non-manifold edges show where there are more than two surfaces sharing an edge, which might indicate incorrect connectivity. For this part, there are yellow edges completely surrounding two areas. This indicates that there are probably duplicate surfaces in these locations. |
| 10. | Select all of the check boxes. |
| 11. | Close the Visualization browser. |
| 12. | To exit the panel, click return. |
| 13. | To shade the model's geometry and surface edges, click  on the Visualization toolbar. on the Visualization toolbar. |
| 14. | To locate any errors in the geometry, rotate, zoom, and pan. |
| 15. | Note the areas to be worked on: |
| • | A surface that overhangs a round corner |
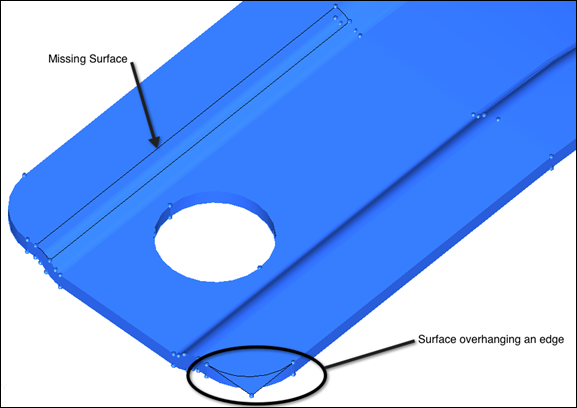
Surface overhanging an edge and a missing surface
Step 3: Delete the surface that overhangs the round corner.
| 1. | To open the Delete panel, click Geometry > Delete > Surfaces from the menu bar, or press F2. |
| 2. | Optional: If you opened the Delete panel by pressing F2, set the entity selector to surfs. |
| 3. | Select the overhanging surface shown in the previous image. |
| 4. | Click delete entity. HyperMesh deletes the selected entities. |
| 5. | To exit the panel, click return. |
Step 4: Create surfaces to fill large gaps in the model.
| 1. | To open the panel from which you can create a surface, click Geometry > Create > Surfaces > Spline/Filler from the menu bar. |
| 2. | Clear the Keep tangency check box. |
| 3. | Set the entity selector to lines. |
| 4. | Verify the Auto create (free edges only) check box is selected. The Auto create option simplifies the selection of the lines bounding the missing surface. Once a line is selected, HyperMesh selects the remaining free edges that form a closed loop, and then creates the filler surface. |
| 5. | Zoom into the area indicated in the following image. |
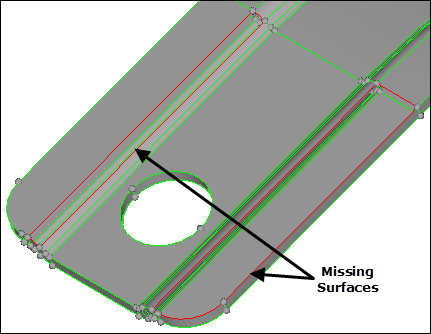
Area of missing surfaces
| 6. | Select one of the red lines bounding one of the gaps (missing surfaces) shown in the previous image. HyperMesh creates a filler surface to close the hole. |
| 7. | Repeat step 4.6 to create a filler surface in the other gap. |
| 8. | To exit the panel, click return. |
Step 5: Set the global geometry cleanup tolerance to .01.
| 1. | Press O. The Options panel opens. |
| 2. | Go to the geometry subpanel. |
| 3. | In the cleanup tol = field, type 0.01 to stitch the surfaces with a gap less than 0.01 |
| 4. | To exit the panel, click return. |
Step 6: Combine multiple free edge pairs at one time with the equivalence tool.
| 1. | From the menu bar, click Geometry > Edit > Surface Edges > Equivalence. |
| 2. | Select the equiv free edges only check box. |
| 4. | Verify that the cleanup tol= is set to 0.01. This is the global cleanup tolerance that you specified in the Options panel. |
| 5. | Click equivalence. HyperMesh combines any free edge pairs within the specified cleanup tolerance. Most of the red free edges are combined into green shared edges. The few remaining are caused by gaps larger than the cleanup tolerance. |
Step 7: Combine free edge pairs, one pair at a time, using the toggle.
| 1. | Go to the toggle subpanel. |
| 2. | In the cleanup tol = field, type 0.1. |
| 3. | Click one of the free edges shown in the following image. When you select the edge, it will change from red to green, indicating that the free edge pair has been equivalenced. |
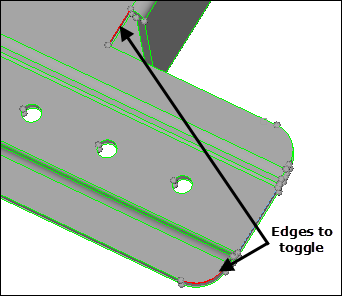
Area where free edges need to be toggled
| 4. | Use toggle to equivalence the other edges shown in the previous image. |
Step 8: Combine the remaining free edge pair using replace.
| 1. | Go to the replace subpanel. |
| 2. | In the Model browser, View folder, right-click on View2 and select Show from the context menu. The graphics area displays two edges to retain and remove for replacement. |
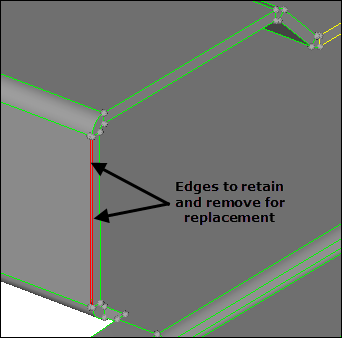
| 3. | With the moved edge line selector active, click the leftmost free edge. |
| 4. | With the retained edge line selector now active, select the rightmost red edge. |
| 5. | In the cleanup tol = field, enter 0.1. |
| 6. | Click replace. HyperMesh posts a message similar to, "Gap = (.200018). Do you still wish to replace?". |
| 7. | To close the gap, click Yes. |
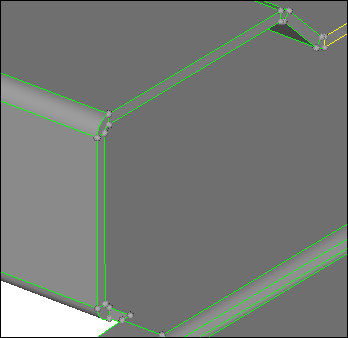
| 8. | To exit the replace subpanel, click return. |
Step 9: Find and delete all duplicate surfaces.
| 1. | From the menu bar, click Geometry > Defeature > Duplicates. |
| 2. | Click surfs >> displayed. |
| 3. | In the cleanup tol = field, type 0.01. |
| 4. | Click find. The status bar displays the following message, "2 duplicated surfaces were found." |
| 5. | To remove duplicate surfaces, click delete. |
Step 10: Observe the model again to identify any remaining free edges, or missing or duplicate surfaces.
| 1. | On the Visualization toolbar, change the geometry color mode to  and click and click  to shade the model's geometry and surface edges. to shade the model's geometry and surface edges. |
| 2. | Observe the model again to identify the remaining free edges and missing or duplicate surfaces. |
| Note: | All of the edges in the model should be displayed as green shared edges, indicating that you have a completely enclosed thin solid part. |
| 3. | To exit the return panel, click return. |
Step 11 (Optional): Save your work.
With the cleanup operations completed, now is a good time to save your work.
| 1. | From the menu bar, click File > Save > Model. |
See Also:
HyperMesh Tutorials














