In this tutorial, you will learn how to:
| • | Load the SAMCEF user profile |
| • | Retrieve the HyperMesh model files for this tutorial |
| • | Define the hypothesis on the elements |
| • | Create an isotropic material |
| • | Assign the property and the material to the elements |
| • | Create loads and the load cases associated with them |
| • | Export the model in SAMCEF format |
Model Files
This tutorial uses the hook.hm file, which can be found in <hm.zip>/interfaces/samcef/. Copy the file(s) from this directory to your working directory.
Exercise
Step 1: Load the SAMCEF user profile
| 1. | Start HyperMesh Desktop. |
| 2. | In the User Profiles dialog, set the user profile to Samcef. |
Step 2: Retrieve the model file
| 1. | Open a model file by clicking File > Open > Model from the menu bar. |
| 2. | In the Open Model dialog, open the file Hook.hm. |
| 3. | On the Visualization toolbar, click  to shade the models elements and mesh lines, if they are not already shaded. to shade the models elements and mesh lines, if they are not already shaded. |
Step 3: Check the hypothesis
| 1. | Open the Element Types panel by clicking Mesh > Assign > Element Types from the menu bar. |
| 2. | Go to the 2D & 3D subpanel. |
| 3. | In this panel, you have the link between the keyword of HyperMesh (tria3, quad4, ...) and the hypothesis of SAMCEF. You can change the hypothesis for each element configuration and also update each element with a different hypothesis. |
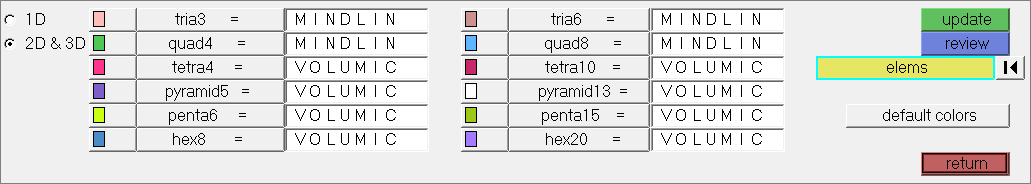
| 4. | Click return to close the panel. |
Step 4: Create the material
| 1. | In the Model browser, right-click and select Create > Material from the context menu. |
| 2. | In the Create Material dialog: |
| • | Set Card image to ISOTROPIC. |
| Note: | You can create different types of elastic material (anisotropic, isotropic or orthotropic). |
| • | Select a color for the material. |
| • | Select the Card edit material upon creation checkbox. |
| • | Select Create. The isotropic card image displays. |
| Note: | If a material property in brackets does not have a value below it, this indicates that it is turned off. Edit these material properties by clicking on the property in the brackets you wish to edit. In the text field that appears below it, enter a value. |
A new material named steel has been created. At any time, the card image for this material can be modified using the card editor.
Step 5: Create the properties and assign it to the elements
| 1. | In the Model browser, right-click and select Create > Property from the context menu. |
| 2. | In the Create Property dialog: |
| • | Set Card image to SHELLPHP. |
| • | Select a color for the property. |
| • | Select the Assign material checkbox. |
| 3. | In the SHELLPHP card image, select the THICK checkbox. |
| 4. | In the THICK field, enter 1.5. |
| 5. | Click return. A new 2D property has been created. |
| 6. | In the Model browser, Component folder, right-click on shell and select Assign from the context menu. |
| 7. | In the Assign to Component(s) dialog: |
| • | Click OK. The property is now assigned to the elements. |
| 8. | Create a property named solid, that is of type 3D, and has a SOLIDMAT card image. You can skip editing the card image for this property, because this 3D property is a dummy property defined to assign material and an ATT number to the elements. |
| 9. | Assign the elements of the component solid to the new 3D property solid. |
| 10. | Check that the properties are correctly assigned to the elements using the By Prop icon  . The elements should have the same color as the properties. . The elements should have the same color as the properties. |
Step 6: Create the load collectors
| 1. | In the Model browser, right-click and select Create > Load Collector from the context menu. |
| 2. | In the Create Load Collector dialog: |
| • | Select a color for the load collector. |
| 3. | Create a second load collector named force. |
Step 7: Create the constraints
| 1. | In the Model browser, Load Collector folder, right-click on spc and select Make Current from the context menu. This sets the spc load collector as the current load collector. |
| 2. | Open the Constraints panel by clicking BCs > Create > Constraints from the menu bar. |
| 3. | Go to the create subpanel. |
| 4. | Using the nodes selector, select the master nodes of the rigid elements, which are defined in the holes of the component solid. |
| 5. | Constrain dof1, dof2, dof3, dof4, dof5 and dof6 by checking all of their checkboxes. Set all of them to a value of 0.0 |
DOFs with a check will be constrained, while DOFs without a check will be free.
DOFs 1, 2 and 3 are x, y, and z translational degrees of freedom.
DOFs 4, 5 and 6 are x, y an z rotational degrees of freedom.
| 6. | Click create to apply these constraints to the selected nodes. |
| 7. | Click return to close the panel. |
Step 8: Create the forces
| 1. | In the Model browser, Load Collector folder, right-click on force and select Make Current from the context menu. This sets the force load collector as the current load collector. |
| 2. | Open the Forces panel by clicking BCs > Create > Forces from the menu bar. |
| 3. | Go to the create subpanel. |
| 4. | Using the nodes selector, select the master nodes of the rigid element. |
| 5. | Set the local system / global system toggle to global system. |
| 6. | Set the vector definition switch to constant vector. |
| 7. | In the magnitude = field, enter 250. |
| 8. | Set the orientation selector to z-axis. |
Step 9: Create a SAMCEF database
| 1. | Open the Load Steps panel by clicking Setup > Create > Load Steps from the menu bar. |
| 2. | In the name field, enter z-force. |
| 3. | Using the loadcols selector, select the load collectors force and spc. |
| 5. | Click return to close the panel. |
Step 10: Export the file
| 1. | From the menu bar, click File > Export > Solver Deck. The Export - Solver Deck tab opens. |
| 2. | In the File field, enter the name of the file as hook.dat. |
| 3. | Set template to Samcef. |
See Also:
HyperMesh Tutorials












