Global Response Surface Method (GRSM) is a response surface based approach. During each iteration, the response surface based optimization generates a few designs. Additional designs are generated globally to ensure a good balance on local search capability and global search capability. Response surface is adaptively updated with the newly generated designs to have a better fit of the model.
Usability Characteristics
| • | GRSM can disposes of both single objective problems and multi-objective problems. |
| • | GRSM is the default method for multi-objective optimization problems. GRSM is also the suggested method when you are solving a single objective optimization problem with a large number of input variables and/or when a global optima is required. |
| • | It is recommend to use GRSM directly on a solver and not on a Fit. If you have a Fit, consider using an Inclusion matrix with your data. |
| • | Consists of a global search capability. |
| • | Supports discrete optimization. |
| • | All the designs generated in one iteration can be solved in parallel. |
| • | If the model analysis is time consuming, then GRSM is a good choice. If the model analysis is quite cheap and a thorough search of the design space is needed (for example, 100000 model evaluations are needed), then GA or MOGA are recommended. |
| • | In the case of a failed run, it is possible to ignore a failed analysis or terminate an optimization. When omitting failed runs, the optimizer randomly generates designs in under-sampled region in order to explore the whole design space effectively. |
| • | Terminates when the maximum number of evaluations (MAXDES) is reached. |
| • | Supports input variable constraints. |
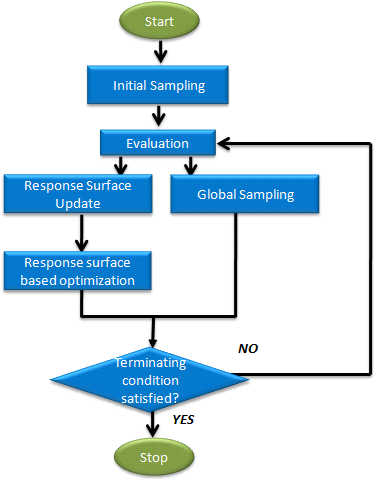
The flowchart below illustrates the different phases of the GRSM process.
Settings
In the Specifications step, you can change the settings of GRSM from the following tabs:
In the Settings tab, you can access the settings listed below. Please note that for most applications the default settings work optimally, and you may only need to change the Number of Evaluations and On Failed Analysis.
Setting
|
Default Value
|
Range
|
Description
|
Number of Evaluations
(MAXDES)
|
50
|
>0
|
Number of evaluations allowed.
|
On failed analysis
(IGFAIL)
|
0
|
0 or 1
|
0 optimizer terminates with an error message when an analysis run fails (default).
1 optimizer ignores the failed analysis run, random generate design, and re-tries the analysis.
|
|
In the More tab, you can access the setting listed below. Please note that for most applications, the default settings work optimally.
Setting
|
Default Value
|
Range
|
Description
|
Initial Sample Points
(NPTGRS)
|
min(20,n+2)
|
Integer
>=0
|
The number of initial sample points.
Default is min(20,n+2) initial sample points; n is the number of input variables;
> 0 use the user defined value.
|
Random Seed
(GAREPT)
|
1
|
Integer
0 to 10000
|
Controlling repeatability of runs depending on the way the sequence of random numbers is generated.
0 random (non-repeatable),
> 0 triggers a new sequence of pseudo-random numbers, repeatable if the same number is specified.
|
Points per Iteration
(PARALLEL)
|
2
|
1 to NPTGRS
|
Number of designs to be evaluated for optimum design search and response surface update.
After the initial NPTGRS designs, PARALLEL designs are generated from response surface based optimization and/or incremental sampling. In the iteration that follows, these designs are used to adaptively update the response surface to have a better fit of the model. Note that these designs can be evaluated in parallel.
|
Constraint violations tol.
(GMAX)
|
0.5
|
> 0.0
|
Global maximum allowable percentage constraint violation. Constraints must not be violated by more than this value in the converged design.
|
Constraint threshold
(EPSCON)
|
1.0e-4
|
> 0.0
|
This parameter is used for constraint value calculation. In general, constraint value is normalized to its bound.
|
Use Inclusion Matrix
(INCLUSI)
|
No
|
No, With Initial, Without Initial
|
| • | No ignores the Inclusion matrix |
| • | With Initial runs the initial point. The inclusion set and initial point are used to build the initial response surface. |
| • | Without Initial does not run the initial point. The inclusion set is used to build the initial response surface. |
|
|








