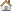In this tutorial you will learn how to create a template file for shape variables and how to import them to HyperStudy. The input variables are three shape variables; xtrans, ytrans and radius. Each of these shapes are created by perturbing the mesh in the corresponding direction by 1 unit.
The sample base input template used in this tutorial can be found in <hst.zip>/HS-1021/. Copy the tutorial files from this directory to your working directory.
|
|
Figure 1: Double Symmetric Plate Model
|
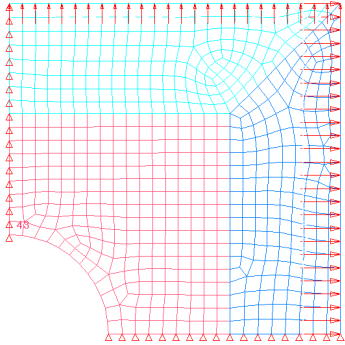
Figure 2: Double Symmetric Plate Model with Shape Vectors
|
| 1. | Start HyperMesh Desktop. |
| 2. | In the User Profiles dialog, set the user profile to OptiStruct. |
| 3. | From the menu bar, click File > Open > Model. |
| 4. | In the Open Model dialog, open the plate_with_shapes.hm file. A model appears in the graphics area. |
| 5. | From the Analysis page, click optimization. |
| 7. | Go to the desvar subpanel. In this subpanel you will create three design variables (XTrans, YTrans and Rad) for three shapes. |
| 8. | Create a design variable. |
| a. | In the desvar= field, enter XTrans. |
| c. | Select the shape, xtrans. |
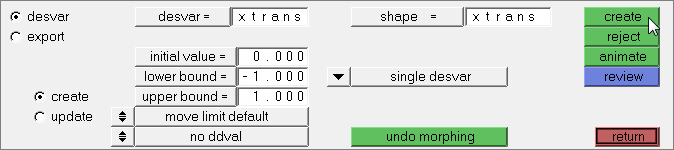
| 9. | Create two more design variables labeled YTrans and Rad. Select the shape ytrans for design variable YTrans, and select the shape radius for design variable Rad. |
| 10. | Go to the export subpanel to export the shape variables. |
| 11. | Set analysis code to HyperStudy. |
| 12. | Set sub-code to OptiStruct. |
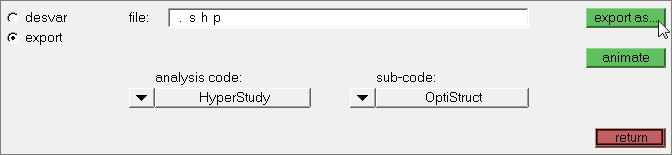
| 14. | In the Save As dialog, save the file as plate_with_shapes.shp. |
| 15. | Quit HyperMesh by clicking File > Exit from the menu bar. |
|
| 2. | From the menu bar, click Tools > Editor. The Editor opens. |
| 3. | In the File field, open the plate_with_shapes.fem file. |
| 4. | In the editor, right-click and select Select Nodes > GRID from the context menu. All of the GRID cards in the plate_with_shapes.fem file highlight. |
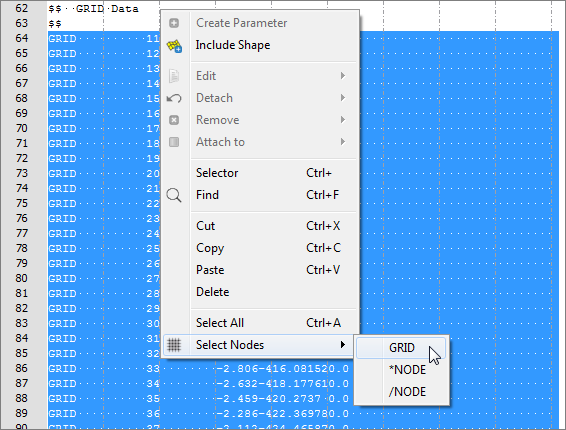
| 5. | Right-click on the highlighted cards and select Include Shape from the context menu. |
| 6. | In the Shape Template dialog, open the plate_with_shapes.optistruct.node.tpl file. |
| 8. | In the Save Template dialog, save the file as plate_with_shapes.tpl. |
|
In this step, you will import the design variables (known as input variables in HyperStudy) created in Step 1: Exporting Shape Variables from HyperMesh to HyperStudy.
| 1. | To start a new study, click File > New from the menu bar, or click  on the toolbar. on the toolbar. |
| 2. | In the HyperStudy – Add dialog, enter a study name, select a location for the study, and click OK. |
| 3. | Go to the Define Models step. |
| 4. | Add a Parameterized File model. |
| a. | From the Directory, drag-and-drop the plate_with_shapes.tpl file into the work area. |
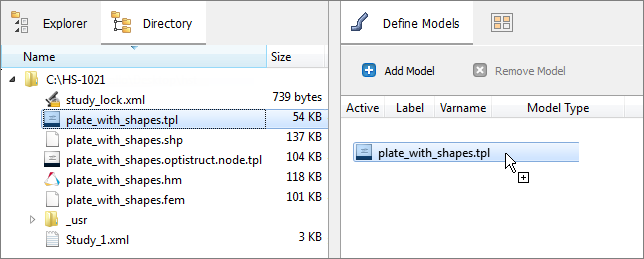
| b. | In the Solver input file column, enter plate.fem. This is the name of the solver input file HyperStudy writes during any evaluation. |
| c. | In the Solver execution script column, select OptiStruct (os). |

| 5. | Click Import Variables. Three input variables are imported from the plate_with_shapes.tpl resource file. |
| 6. | Go to the Define Input Variables step. |
| 7. | Review the input variable's lower and upper bound ranges. |
| 8. | Go to the Specifications step. |
|
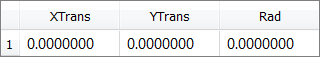
| 1. | In the work area, set the Mode to Nominal Run or System Bound Check. |
A Nominal Run performs one run, and sets the input variable's values to their initial values.
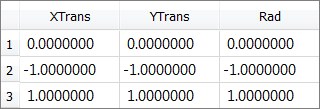
A System Bound Check performs three runs, and sets all of the input variable's values to their initial, lower bound and upper bound values.
| 3. | Go to the Evaluate step. |
| 5. | Go to the Define Output Responses step. |
|
In this step you will create two output responses: Mass and Displacement.
| 1. | Create the Mass output response. |
| a. | From the Directory, drag-and-drop the plate.out file, located in approaches/nom_1/run_00001/m_1, into the work area. |
| b. | In the File Assistant dialog, set the Reading technology to Altair® HyperWorks® and click Next. |
| c. | Select Single item in a time series, then click Next. |
| d. | Define the following options, and then click Next. |
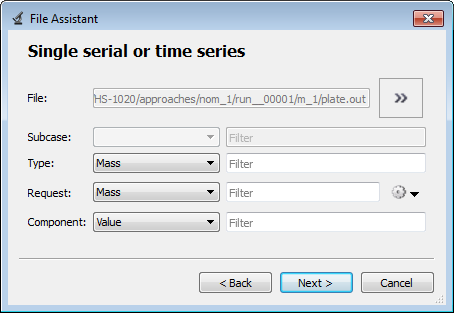
| e. | Label the output response Mass. |
| f. | Set Expression to First Element. |
| Note: | Because there is only a single value in this vector, [0] is inserted after v_1, thereby choosing the first (and only) entry in the vector. |
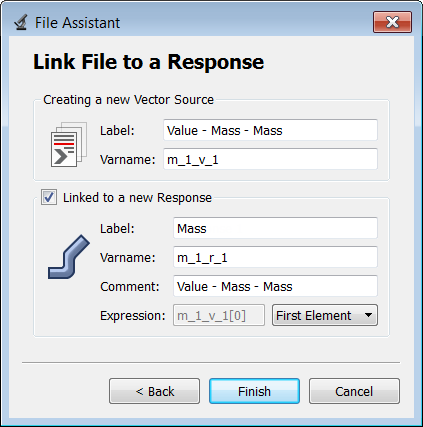
| g. | Click Finish. The Mass output response is added to the work area. |
| 2. | Create the Displacement output response. |
| a. | From the Directory, drag-and-drop the plate.h3d file, located in approaches/nom_1/run_00001/m_1, into the work area. |
| b. | In the File Assistant dialog, set the Reading technology to Altair® HyperWorks® and click Next. |
| c. | Select Single item in a time series, then click Next. |
| d. | Define the following options, and then click Next. |
| • | Set Subcase to Subcase 1 (Load). |
| • | Set Type to Displacement (Grids). |
| e. | Label the output response Displacement. |
| f. | Set Expression to First Element. |
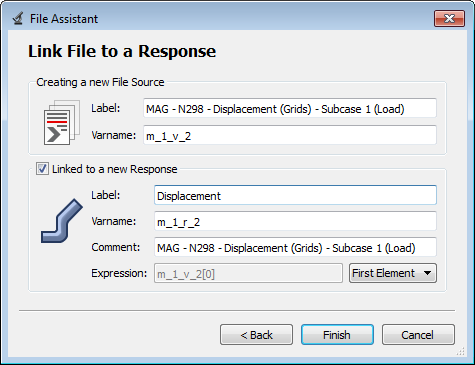
| g. | Click Finish. The Displacement output response is added to the work area. |
| 3. | Click Evaluate to extract the output response values. |
| 4. | Proceed to the desired study type (DOE, Optimization, of Stochastic study). |
|
See Also:
HyperStudy Tutorials