Latin Hypercube |

|

|

|

|
|
Latin Hypercube |

|

|

|

|
The Latin Hypercube method, developed by McKay, Conover, and Beckman (1979), is an approach which can yield precise estimates of output statistics with a lesser number of samples than simple random sampling. The Latin Hypercube method uses a constrained or stratified sampling scheme.
Latin Hypercube sampling selects ![]() different values from each of
different values from each of ![]() variables
variables ![]() 1, …
1, … ![]()
![]() in the following manner:
in the following manner:
| • | The range of each random variable is divided into |
| • | One value from each interval is selected at random with respect to the probability density in the interval. |
| • | The |
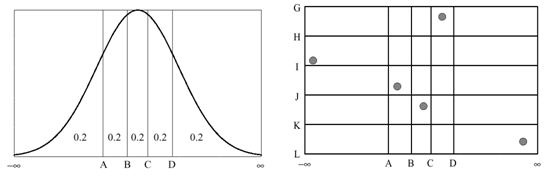
Figure 1: Illustration of Latin Hypercube Sampling
| • | A stratified sampling scheme like Latin Hypercube offers the advantage of selecting random variable values that are uniformly spread across the range of random variables while taking into account the probability density function of those random variables. |
| • | A correlation structure can be specified to reflect the correlation existing between random variables. Applying a correlation structure can be costly for a large number of input variables. |
In the Specifications step, you can change the following settings of Latin Hypercube from the Settings tab.
Parameter |
Default |
Range |
Description |
Number of runs(npt) |
100 |
> 0 |
Number of designs to be evaluated. |
Random Seed(iseed) |
1 |
Integer 0 to 10000 |
Controlling repeatability of runs depending on the way the sequence of random numbers is generated. 0 random (non-repeatable) > 0 triggers a new sequence of pseudo-random numbers, repeatable if the same number is specified. |
Apply User Correlations |
true |
true or false |
Apply user specified correlations on the data. |