Simple Random |

|

|

|

|
|
Simple Random |

|

|

|

|
The conventional approach of sampling is commonly called Simple Random or Monte Carlo. In Simple Random sampling, a pseudo-random number generator is used for generating random numbers from 0 to 1. Design points are generated by using the Inverse Transform method. Because the sequence of samples is random, clustering may occur in the design point distribution.
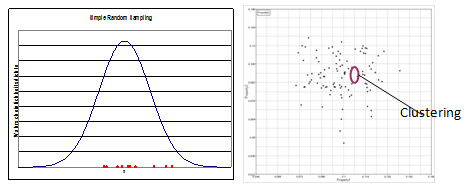
Figure 1: Illustration of Simple Random Sampling
| • | The statistical measures (such as mean or standard deviation) of a random sample group requires large numbers of runs to converge the given probability distribution’s statistical measures. |
| • | A correlation structure can be specified to reflect the correlation existing between random variables. Applying a correlation structure can be costly for a large number of input variables. |
In the Specifications step, you can change the following settings of Simple Random from the Settings tab.
Parameter |
Default |
Range |
Description |
Number of Runs(npt) |
100 |
> 0 |
Number of designs to be evaluated. |
Random Seed(iseed) |
1 |
Integer 0 to 10000 |
Controlling repeatability of runs depending on the way the sequence of random numbers is generated. 0 random (non-repeatable) > 0 triggers a new sequence of pseudo-random numbers, repeatable if the same number is specified. |
Apply User Correlations |
true |
true or false |
Apply user specified correlations on the data. |