Reliability and Robustness Assessment |

|

|

|

|
|
Reliability and Robustness Assessment |

|

|

|

|
Computational methods to estimate reliability fall into two categories as analytical methods and sampling-based methods.
| • | Analytical methods use sensitivity information and they construct approximations of the limit state. First-order reliability method (FORM), second-order reliability method (SORM), advanced mean value methods (AMV) are some of the popular analytical methods. |
| • | Sampling-based methods are also called Monte Carlo Methods. Sampling-based methods generate many random samples and evaluate whether performance function is violated. They typically use random numbers; the ones that do not use random numbers are called quasi Monte Carlo methods |
In HyperStudy there are three sampling-based methods for reliability and robustness assessment. These are Simple random sampling, Latin hypercube sampling and Hammersley sampling. The first two are based on pseudo-random numbers whereas the last one is based on deterministic points. In this section, these three methods are explained after a description of parameter distributions types available in HyperStudy.
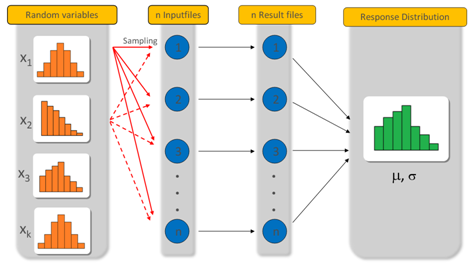
Position of the sampling in the stochastic analysis
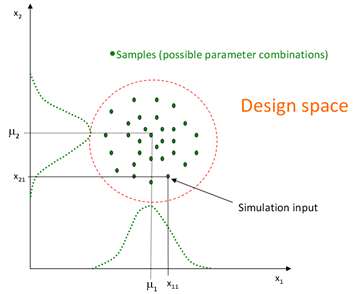
Illustration of the sampling