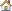The evaluation stresses (normal, shear, and von Mises) for each bar element are listed in the links provided below. The shear stress includes torsion and shear.
Bar Element Types
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
|
|
S2N
|
|
|
S3N
|
|
|
S4N
|
|
|
|
S5S
|
S5V
|
|
S6S
|
S6V
|
|
S7S
|
S7V
|
|
S8S
|
S8V
|
SNMAX
|
SSMAX
|
SVMAX
|
|
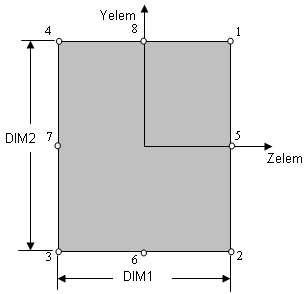
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
S1S
|
S1V
|
S2N
|
S2S
|
S2V
|
S3N
|
S3S
|
S3V
|
S4N
|
S4S
|
S4V
|
|
S5S
|
S5V
|
|
S6S
|
S6V
|
|
S7S
|
S7V
|
|
S8S
|
S8V
|
|
S9S
|
S9V
|
|
S10S
|
S10V
|
|
S11S
|
S11V
|
|
S12S
|
S12V
|
SNMAX
|
SSMAX
|
SVMAX
|
Several stress recovery points are coincident (for example, 1 and 5, 2 and 6). In these cases, the lower number refers to stress recovered in the xy plane and the higher number refers to stress recovered in the xz plane.
|
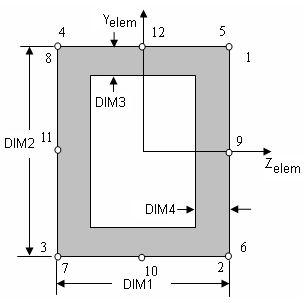
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
S1S
|
S1V
|
S2N
|
S2S
|
S2V
|
S3N
|
S3S
|
S3V
|
S4N
|
S4S
|
S4V
|
|
S5S
|
S5V
|
|
S6S
|
S6V
|
|
S7S
|
S7V
|
|
S8S
|
S8V
|
|
S9S
|
S9V
|
|
S10S
|
S10V
|
|
S11S
|
S11V
|
|
S12S
|
S12V
|
SNMAX
|
SSMAX
|
SVMAX
|
Several stress recovery points are coincident (for example, 1 and 5, 2 and 6). In these cases, the lower number refers to stress recovered in the xy plane and the higher number refers to stress recovered in the xz plane.
|
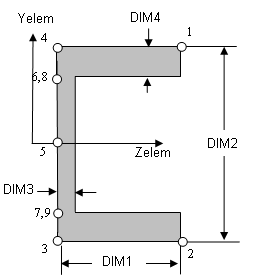
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
|
|
S2N
|
|
|
S3N
|
|
|
S4N
|
|
|
|
S5S
|
S5V
|
|
S6S
|
S6V
|
|
S7S
|
S7V
|
|
S8S
|
S8V
|
|
S9S
|
S9V
|
SNMAX
|
SSMAX
|
SVMAX
|
Several stress recovery points are coincident (for example, 1 and 5, 2 and 6). In these cases, the lower number refers to stress recovered in the xy plane and the higher number refers to stress recovered in the xz plane.
|
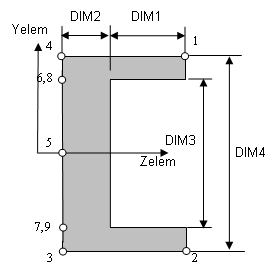
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
|
|
S2N
|
|
|
S3N
|
|
|
S4N
|
|
|
|
S5S
|
S5V
|
|
S6S
|
S6V
|
|
S7S
|
S7V
|
|
S8S
|
S8V
|
|
S9S
|
S9V
|
SNMAX
|
SSMAX
|
SVMAX
|
Several stress recovery points are coincident (for example, 1 and 5, 2 and 6). In these cases, the lower number refers to stress recovered in the xy plane and the higher number refers to stress recovered in the xz plane.
|
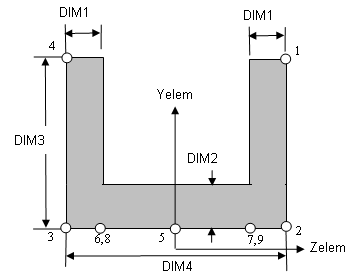
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
|
|
S2N
|
|
|
S3N
|
|
|
S4N
|
|
|
|
S5S
|
S5V
|
|
S6S
|
S6V
|
|
S7S
|
S7V
|
|
S8S
|
S8V
|
|
S9S
|
S9V
|
SNMAX
|
SSMAX
|
SVMAX
|
Several stress recovery points are coincident (for example, 1 and 5, 2 and 6). In these cases, the lower number refers to stress recovered in the xy plane and the higher number refers to stress recovered in the xz plane.
|
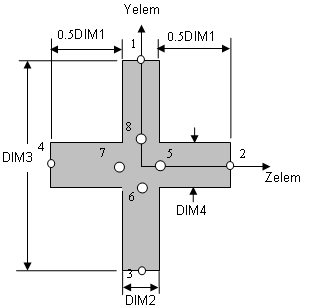
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
|
S1V
|
S2N
|
|
S2V
|
S3N
|
|
S3V
|
S4N
|
|
S4V
|
|
S5S
|
S5V
|
|
S6S
|
S6V
|
|
S7S
|
S7V
|
|
S8S
|
S8V
|
SNMAX
|
SSMAX
|
SVMAX
|
Several stress recovery points are coincident (for example, 1 and 5, 2 and 6). In these cases, the lower number refers to stress recovered in the xy plane and the higher number refers to stress recovered in the xz plane.
|
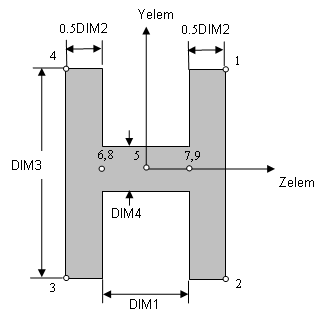
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
|
|
S2N
|
|
|
S3N
|
|
|
S4N
|
|
|
|
S5S
|
S5V
|
|
S6S
|
S6V
|
|
S7S
|
S7V
|
|
S8S
|
S8V
|
|
S9S
|
S9V
|
SNMAX
|
SSMAX
|
SVMAX
|
Several stress recovery points are coincident (for example, 1 and 5, 2 and 6). In these cases, the lower number refers to stress recovered in the xy plane and the higher number refers to stress recovered in the xz plane.
|
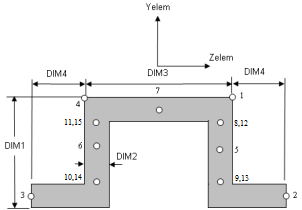
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
|
|
S2N
|
|
|
S3N
|
|
|
S4N
|
|
|
|
S5S
|
S5V
|
|
S6S
|
S6V
|
|
S7S
|
S7V
|
|
S8S
|
S8V
|
|
S9S
|
S9V
|
|
S10S
|
S10V
|
|
S11S
|
S11V
|
|
S12S
|
S12V
|
|
S13S
|
S13V
|
|
S14S
|
S14V
|
|
S15S
|
S15V
|
SNMAX
|
SSMAX
|
SVMAX
|
Several stress recovery points are coincident (for example, 1 and 5, 2 and 6). In these cases, the lower number refers to stress recovered in the xy plane and the higher number refers to stress recovered in the xz plane.
|
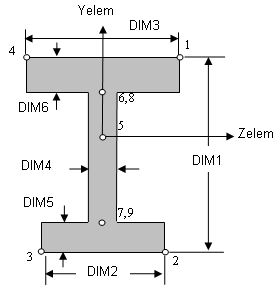
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
|
|
S2N
|
|
|
S3N
|
|
|
S4N
|
|
|
|
S5S
|
S5V
|
|
S6S
|
S6V
|
|
S7S
|
S7V
|
|
S8S
|
S8V
|
|
S9S
|
S9V
|
SNMAX
|
SSMAX
|
SVMAX
|
Several stress recovery points are coincident (for example, 1 and 5, 2 and 6). In these cases, the lower number refers to stress recovered in the xy plane and the higher number refers to stress recovered in the xz plane.
|
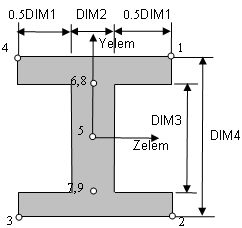
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
|
|
S2N
|
|
|
S3N
|
|
|
S4N
|
|
|
|
S5S
|
S5V
|
|
S6S
|
S6V
|
|
S7S
|
S7V
|
|
S8S
|
S8V
|
|
S9S
|
S9V
|
SNMAX
|
SSMAX
|
SVMAX
|
Several stress recovery points are coincident (for example, 1 and 5, 2 and 6). In these cases, the lower number refers to stress recovered in the xy plane and the higher number refers to stress recovered in the xz plane.
|
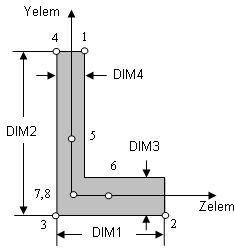
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
|
|
S2N
|
|
|
S3N
|
|
|
S4N
|
|
|
|
S5S
|
S5V
|
|
S6S
|
S6V
|
|
S7S
|
S7V
|
|
S8S
|
S8V
|
SNMAX
|
SSMAX
|
SVMAX
|
Several stress recovery points are coincident (for example, 1 and 5, 2 and 6). In these cases, the lower number refers to stress recovered in the xy plane and the higher number refers to stress recovered in the xz plane.
|
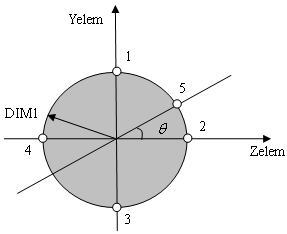
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
S1S
|
|
S2N
|
S2S
|
|
S3N
|
S3S
|
|
S4N
|
S4S
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S5V
|
The location of point 5 will be determined by varying the  from 0 to 360 degrees to find the maximum von Mises stress. from 0 to 360 degrees to find the maximum von Mises stress.
|
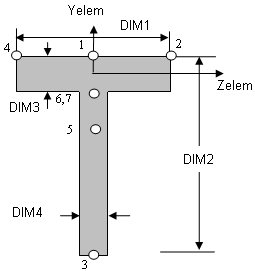
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
|
|
S2N
|
|
|
S3N
|
|
|
S4N
|
|
|
|
S5S
|
S5V
|
|
S6S
|
S6V
|
|
S7S
|
S7V
|
SNMAX
|
SSMAX
|
SVMAX
|
Several stress recovery points are coincident (for example, 1 and 5, 2 and 6). In these cases, the lower number refers to stress recovered in the xy plane and the higher number refers to stress recovered in the xz plane.
|
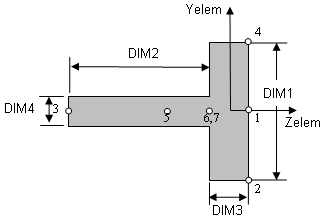
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
|
|
S2N
|
|
|
S3N
|
|
|
S4N
|
|
|
|
S5S
|
S5V
|
|
S6S
|
S6V
|
|
S7S
|
S7V
|
SNMAX
|
SSMAX
|
SVMAX
|
Several stress recovery points are coincident (for example, 1 and 5, 2 and 6). In these cases, the lower number refers to stress recovered in the xy plane and the higher number refers to stress recovered in the xz plane.
|
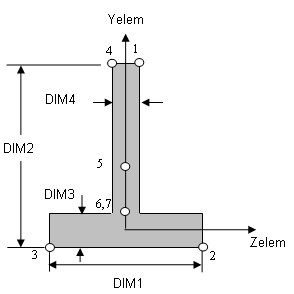
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
|
|
S2N
|
|
|
S3N
|
|
|
S4N
|
|
|
|
S5S
|
S5V
|
|
S6S
|
S6V
|
|
S7S
|
S7V
|
SNMAX
|
SSMAX
|
SVMAX
|
Several stress recovery points are coincident (for example, 1 and 5, 2 and 6). In these cases, the lower number refers to stress recovered in the xy plane and the higher number refers to stress recovered in the xz plane.
|
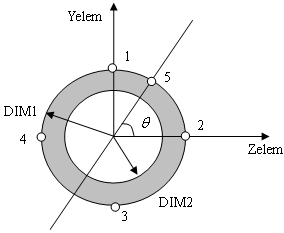
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
S1S
|
|
S2N
|
S2S
|
|
S3N
|
S3S
|
|
S4N
|
S4S
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
S5V
|
The location of point 5 will be determined by varying the  from 0 to 360 degrees to find the maximum von Mises stress. from 0 to 360 degrees to find the maximum von Mises stress.
|
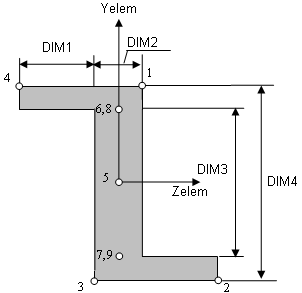
Cross-sectional dimensions and stress constraint evaluation points
Evaluation Stresses
Normal Stress
|
Shear Stress
|
von Mises Stress
|
S1N
|
|
|
S2N
|
|
|
S3N
|
|
|
S4N
|
|
|
|
S5S
|
S5V
|
|
S6S
|
S6V
|
|
S7S
|
S7V
|
|
S8S
|
S8V
|
|
S9S
|
S9V
|
SNMAX
|
SSMAX
|
SVMAX
|
Several stress recovery points are coincident (for example, 1 and 5, 2 and 6). In these cases, the lower number refers to stress recovered in the xy plane and the higher number refers to stress recovered in the xz plane.
|