Hourglass Formulations |

|

|

|

|
|
Hourglass Formulations |

|

|

|

|
Under-integrated elements are very familiar in crash worthiness. In these elements, a reduced number of integration points are used to decrease the computation time. This simplification generates zero energy deformation modes, called hourglass modes. As shown in Fig. 2.18 for an anti-symmetric deformation of a shell element with one integration point at the center, a zero energy mode can be found for a physical deformation mode. That cannot be true from a physical point of view and must be corrected. For a shell mesh, the two main hourglass modes are in-plane (membrane mode) and out-of-plane (W mode).
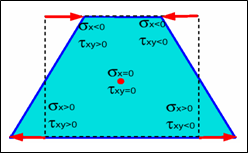
Fig. 2.18: Zero energy mode generation for a reduced integrated shell
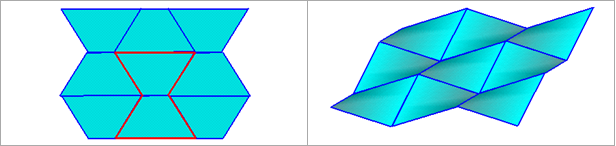
Fig. 2.19: In-plane and out-of-plane hourglass modes
The two correcting methods available are:
| • | Perturbation or penalty method: Hourglass control by application of anti-hourglass forces to maintain deformation stability of the element (historical method). |
| • | Physical stabilization method: Hourglass control by the correction of internal energy in an analytical way. |
For the first method, four formulations are available in RADIOSS:
| • | Type 1 (Default option): Only in-plane modes are corrected, valid for shells and solids. |
| • | Type 2: Old formulation no longer recommended. |
| • | Type 3: Plasticity is taken into account in the computation of anti-hourglass forces; in-plane and out-of-plane hourglass modes are corrected; available only for shells. |
| • | Type 4: Like Type 1 with additional higher order terms in the computation of anti-hourglass forces and with out-of-plane hourglass mode correction; available only for shells. |
The second method is powerful and can be used when the mesh quality is good. The physical stabilization method is incorporated in the following RADIOSS elements:
| • | QEPH shell |
| • | HEPH solid |
| • | HSEPH solid-shell |
The choice of hourglass formulation plays an essential role on the quality of results. If the mesh is fine enough, the physical stabilization method can be used. Otherwise, Type 3 and Type 4 formulations are recommended for shell meshes. When the material undergoes elastic-plastic behavior, the Type 3 formulation is much more efficient. The hourglass coefficient, hm and hf are recommended to be set to 0.1; however, the default value, hf =0.01 can be used for hr.