Microstructure Predictions |

|

|

|

|
|
Microstructure Predictions |

|

|

|

|
One of the key benefits of HX-Forge solver is the ability to predict Microstructure. During hot deformation process, the billet may undergo recrystallization through any of the recrystallization mechanisms, namely, static, dynamic and meta-dynamic recrystallization. Dynamic recrystallization usually occurs during deformation where as static or meta-dynamic recrystallization takes place post deformation. In HX-forge solver, grain size is calculated as a post processing step using one of the above mentioned recrystallization mechanisms. Most commonly used Avrami type semi-empirical models that express grain size as functions of initial grain size, strain, strain rate and temperature are used in microstructure computations. These models are described below.
The grain size during dynamic recrystallization is calculated using
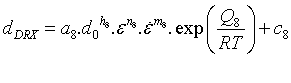
Dynamically recrystallized fraction is given by
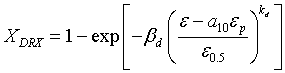
Where ![]() is strain for 50% recrystallization and is given by
is strain for 50% recrystallization and is given by
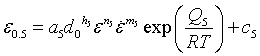
And peak strain corresponds to maximum flow stress is given by
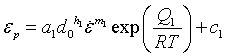
The average grain size after dynamic recrystallization is calculated using
![]()
The grain size during static recrystallization is calculated using
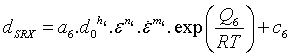
Statically recrystallized fraction is given by
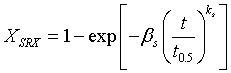
where ![]() is time constant for 50% recrystallization and is given by
is time constant for 50% recrystallization and is given by
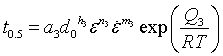
The average grain size after static recrystallization is calculated using
![]()
The grain size during meta-dynamic recrystallization is calculated using
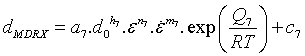
Meta-dynamically recrystallized fraction is given by
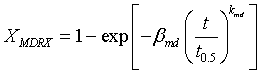
where ![]() is time constant for 50% recrystallization and is given by
is time constant for 50% recrystallization and is given by
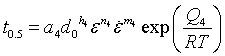
The average grain size after meta-dynamic recrystallization is calculated using
![]()
In the above expressions, ![]() are material coefficients
are material coefficients

In HX-Solver, yield strength is calculated using Hall-Petch equation

In HX-Forge, although GUI to specify the data relevant to microstructure is not available at present (planned for future release), user can specify this data by manually editing the *.grf file. The data format required by HX-Forge solver is described below.
BEGIN PROBLEMDATA
MicrostructureData GSData {
# Initial Grainsize in microns
InitialGrainSize = 250
# Universal Gas Constant R in J/mol.K
UniversalGasConstant = 8.314
GrainSizeModelType = "MetadynamicRX"
MDRXModel = "MDRX_Data"
YieldStrengthModelType = "Hall_Petch"
YieldStrengthModel = "Yield_Data"
}
MDRXGrainSizeData MDRX_Data {
A = 0.0001
a4 = 5.043E-09
a7 = 4.85E+10
b1 = 250
b2 = 1
c7 = 0.0
h4 = 0.0
h7 = 0.0
n4 = -1.42
n7 = -0.41
m4 = -0.408
m7 = -0.028
Q2 = 0
Q4 = 196000
Q7 = -240000
beta_mdrx = 0.693
k_mdrx = 1.0
}
YieldStrengthData Yield_Data {
sigma0 = 25.0
ky = 0.5
# sigma0 is in MPa
# ky is in MN m^-3/2
}
END
The different input parameters in the above data packet for microstructure predictions are explained below:
MicrostructureData is a keyword used to represent the data that include details about the recrystallization model, yield strength model and the associated material coefficients.
InitialGrainSize:
Initial grain size should be prescribed in microns.
UniversalGasConstant:
Always 8.314 J/mol. K
GrainSizeModelType:
For this parameter, user specifies a character string correspond to one of the recrystallization models described above as the model for grain size calculations.
The allowed values and corresponding recrystallization models are given below:
GrainSizeModelType = “StaticRX” – Static Recrystallization Model
GrainSizeModelType = “DynamicRX” – Dynamic Recrystallization Model used
GrainSizeModelType = “MetaDynamicRX” – Meta-dynamic Recrystallization Model
Once the GrainSizeModelType is set, user should specify the material coefficients data for the respective recrystallization model. In the above example, GrainSizeModelType is set as “MetadynamicRX”, hence the solver expects the user to specify MDRXModel and the material coefficients data required for this model MDRXGrainSizeData as a separate data packet.
Meta-dynamic Recrystallization data example:
GrainSizeModelType = “MetaDynamicRX”
MDRXModel = "MDRX_Data"
MDRXGrainSizeData MDRX_Data {
A = 0.0001
a4 = 5.043E-09
a7 = 4.85E+10
b1 = 250
b2 = 1
c7 = 0.0
h4 = 0.0
h7 = 0.0
n4 = -1.42
n7 = -0.41
m4 = -0.408
m7 = -0.028
Q2 = 0
Q4 = 196000
Q7 = -240000
beta_mdrx = 0.693
k_mdrx = 1.0
}
Static Recrystallization data example:
GrainSizeModelType = “StaticRX”
SRXModel = "SRX_Data"
SRXGrainSizeData SRX_Data {
A = 1000
a3 = 3.16
a6 = 678.0
b1 = 250
b2 = 1
c6 = 0.0
h3 = 0.0
h6 = 0.0
n3 = -0.75
n6 = 0.0
m3 = 0.0
m6 = 0.0
Q2 = 0
Q3 = 74826
Q6 = -31710
beta_srx = 0.0
k_srx = 1.0
}
Dynamic Recrystallization data example:
GrainSizeModelType = “DynamicRX”
DRXModel = "DRX_Data"
DRXGrainSizeData DRX_Data {
a1 = 0
a2 = 0.0
a5 = 0.0
a8 = 8.26E09
c1 = 0.0
c5 = 0.0
c8 = 0.0
h1 = 0.0
h5 = 0.0
h8 =1.0
n1 = 0.0
n5 = 0.0
n8 = -0.420
m1 = 0.0
m5 =0.0
m8 = 0.046
Q1 = 0
Q5 =0.0
Q8 = 0.0
beta_drx = 0.0
k_drx = 0.0
}
Yield Strength data example:
YieldStrengthData Yield_Data {
sigma0 = 25.0
ky = 0.5
# sigma0 is in MPa
# ky is in MN m^-3/2