Rear Quad-Link |

|

|

|

|
|
Rear Quad-Link |

|

|

|

|
A Rear Quad-link suspension is included in the Vehicle Library. The Quad-link suspension derives its name from the fact that it is made up of four links. The MotionView Rear Quad-link suspension contains three individual links in tension compression and a strut. This suspension offers flexibility to the designer when determining individual handling parameters, and it is generally used on cars and light trucks.
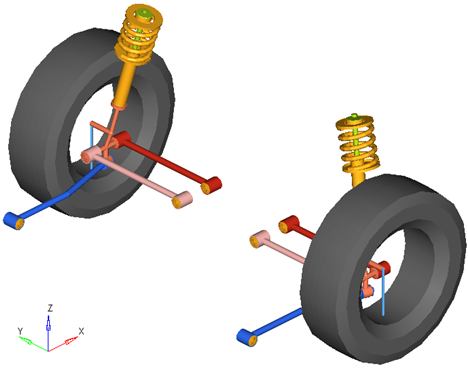
Rear Quad-link Suspension
In conventional designs, the strut is connected to the knuckle and is load bearing (and carries most of the load). The links on the other hand, help in determining suspension geometry and carry much less load.
The Rear Quad-link suspension offers a standard set of attachments, options, and properties that you can set by selecting the suspension system in the Project Browser to display the System/Assembly panel.
Attachments determine how the suspension system attaches to remainder of the vehicle. The Rear Quad-link includes attachments for the front lower link, rear lower link, and the tension strut link:
| • | The front and rear lower links attach to the sub-frame by default. When a sub-frame is not present in the model, the Assembly Wizard attaches both lower links to the vehicle body. If the vehicle body is not present, for example in a half vehicle model, then the Assembly Wizard will attach the lower links to ground. You can set the attachment for the lower links using the Attachment Wizard from the Model menu, or by selecting the Rear quad-link suspension system in the Project Browser and revising the attachments within the Attachments tab on the System/Assembly panel. |
| • | The tension strut attaches to the vehicle body by default. When a vehicle body is not present, the Assembly Wizard attaches the tension strut to ground. The tension strut attachment can be set as you desire using the Attachment Wizard, or by selecting the Rear quad-link suspension in the Project Browser and revising the attachments within the Attachments tab on the System/Assembly panel. |
The Rear quad-link suspension like all Vehicle Library suspension systems includes a Compliant option. When the Rear quad-link suspension’s Compliant option is set to No, the compliant ball joints that act as bushings are changed to non-compliant joints and behave as pure ball joints. Similarly, the front and rear compliant universal joints that act as bushings for the front and rear links are changed to non-compliant joints and behave as pure universal joints. The same is the case for the tension strut bushing.
The Rear quad-link suspension also includes a Spindle compliance option. When the Spindle compliance option is set to Yes, the wheel body connects to the wheel hub via a universal joint and bushing. The universal joint allows camber and toe deflection of the wheel relative to the wheel hub. The wheel hub bushing’s Kx and Ky rates determine the amount of spindle compliance introduced.
The Rear quad-link suspension includes a static alignment dataset and form holding toe and camber variables that determine the orientation of the wheel relative to the knuckle and body in the Global coordinate system. The toe and camber variable values control the location of the spindle align point relative to the wheel center point through parametric expressions. You can view these expressions by selecting the spindle align point and examining its X, Y, and Z locations.
To set the values for toe and camber, select either the static alignment dataset or form and alter the values of the toe and camber variables. Note that the left and right wheels’ toe and camber values must be symmetric. You cannot set the toe and camber angles independently for the two wheels.
Select options using the Assembly Wizard to include stabilizer bar, strut, jounce bumper, or rebound bumper subsystems in the model. You can also select where the subsystem acts, for example whether the rebound bumper is internal to the shock absorber or external.
When you finish creating your model using the Assembly Wizard, the subsystems you have chosen show in the Project Browser as children of the Rear quad-link suspension. The table below shows the optional subsystems available with the Rear quad-link suspension:
Subsystem |
Options |
Stabilizer Bar |
None |
Stabilizer Bar |
Two (2) Piece Bar |
Deformable Rod with |
Strut |
None |
With Inline Joints |
With Cylindrical Joints |
|
Jounce Bumper |
None |
Internal to Shock |
External Jounce Bumper |
|
Rebound Bumper |
None |
Internal to Shock |
External Rebound Bumper |
|
| • | Internal jounce and rebound bumpers act between the shock absorber piston and tube. |
| • | External jounce and rebound bumpers act between the lower links and the Vehicle Body. |
| • | Suspensions created without a spring or a shock absorber subsystem will not function in a full vehicle analysis. |
| • | You can alter how optional subsystems attach to the suspension by selecting the subsystem in the Project Browser and altering the subsystem’s attachments. |
Points locate the joints and bushings in the suspension model. The image below shows the principal points for the Rear quad-link suspension:
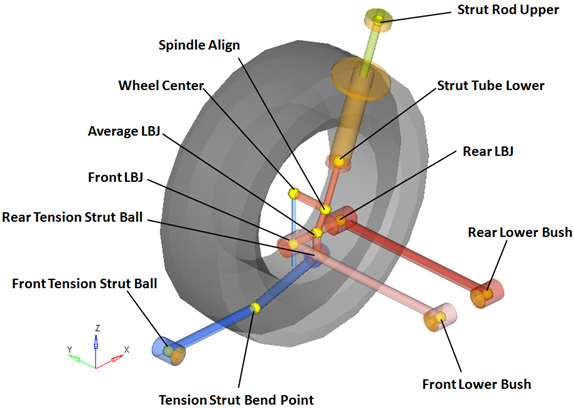
Right Side Principal Points – Rear Multi-link Suspension
| Note | The image above omits the left side of the suspension, points locating body centers of mass, and points that locate the optional subsystems (springs, dampers, bump stops and stabilizer bar) for clarity. |
The Rear Quad-link suspension is comprised of the bodies shown in the image below:
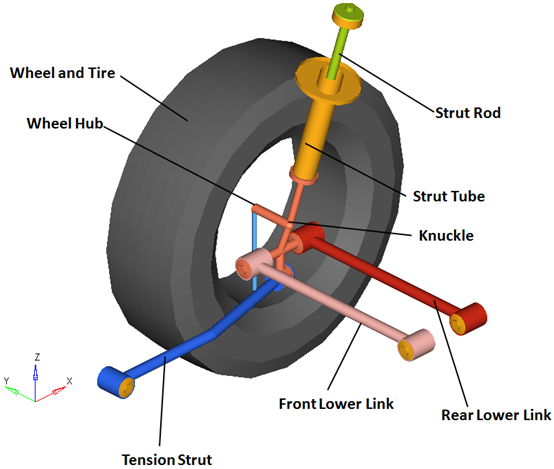
Right Side Bodies – Rear Quad-link Suspension
| Note | The wheel hub body has no associated graphics and therefore is not visible in the image above. |
Optional subsystems may add bodies to the suspension, for example the shock absorber adds two bodies: a shock rod and shock tube. Any bodies added by optional subsystems have been omitted from the image above for clarity.
The table below describes the bodies, bushings, and joints for the Rear Quad-link suspension:
| Note | The table omits the left side joints for clarity. |
Label |
Type |
Body 1 |
Body 2 |
Point |
Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Front Outer |
Spherical |
Front Lower Link |
Knuckle |
Front Lower Ball Joint |
When the Compliant option is set to No, the compliance for this joint is turned "Off" and behaves as a pure spherical joint. |
Rear Outer Bush |
Spherical |
Rear Lower Link |
Knuckle |
Rear Lower Ball Joint |
When the Compliant option is set to No, the compliance for this joint is turned "Off" and behaves as a pure spherical joint. |
Tension Strut Front Bush |
Universal |
Tension Strut |
Subframe, Vehicle Body or Ground |
Front Tension Strut Ball |
When the Compliant option is set to No, the compliance for this joint is turned "Off" and behaves as a pure universal joint. |
Rear Tension Strut Bush |
Universal |
Tension Strut |
Knuckle |
Rear Tension Strut Ball |
When the Compliant option is set to No, the compliance for this joint is turned "Off" and behaves as a pure spherical joint. |
Wheel Spindle |
Revolute |
Wheel Hub |
Knuckle |
Wheel Center |
---- |
Wheel Hub |
Fixed-Joint |
Wheel |
Wheel Hub |
Wheel Center |
When the Spindle compliance option is set to Yes, the joint type changes to universal. |
Front Lower Bush |
Universal |
Front Lower Link |
Subframe, Vehicle Body or Ground |
Front Lower Bush |
When the Compliant option is set to No, the compliance for this joint is turned "Off" and behaves as a pure universal joint. |
Rear Lower Bush |
Universal |
Rear Lower Link |
Subframe, Vehicle Body or Ground |
Rear Lower Bush |
When the Compliant option is set to No, the compliance for this joint is turned "Off" and behaves as a pure universal joint. |
The figure below shows the location of the joints and bushings in the suspension:
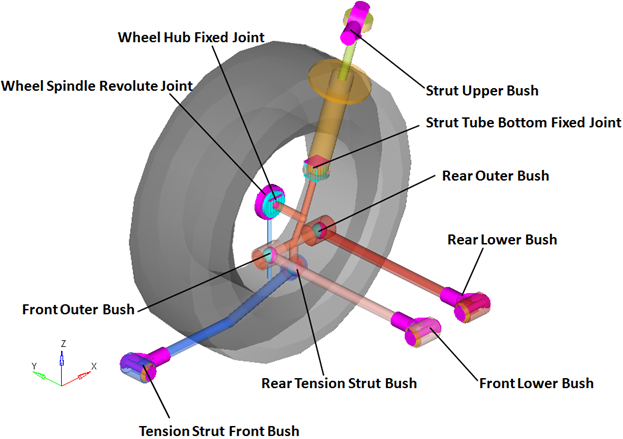
Right Side Joints and Bushings: Rear Quad-link Suspension
The Rear quad-link suspension system can be used in either a half car or a full vehicle analysis. The default geometry and mass is that of a passenger car or light truck, however the model and data can be revised to reflect any size vehicle, from a large truck to a scale model car.
| • | The wheel body represents the mass and inertia of the tire and the rim. |
| • | The wheel hub body represents the mass and inertia of other rotating bodies such as a brake rotor, but not the half-shafts if the suspension is driven. The wheel hub and brake rotor have no associated graphics. |
| • | The wheel and wheel hub parts use the Wheel CG location as the center of gravity. |
| • | Each body’s Center of Gravity (CG) is estimated from the body’s geometry. The formulas are coded into the Point panel and can be seen via the graphical user interface. If more accurate CG locations are available (from a solid model or testing), they should be entered as X, Y, Z coordinates instead of the estimated number. |
| • | A wide variety of combinations of suspensions and subsystems can be built using the Assembly Wizard. You are encouraged to build systems and understand the resulting model using the graphical user interface. |
| • | When building a new suspension model, build the model with all of the optional systems (stabilizer bar, etc) included in the model. Immediately turn off the systems via the Project Browser and run an analysis on the base suspension to ensure it solves properly. As data becomes available for the optional systems, activate those systems and populate them with data. |

Rear-Half-Vehicle Model Employing a Quad-link Suspension
The image below shows the MotionView Project Browser view of the systems in a fully populated rear suspension model. The Rear quadlink suspension system has four “child” systems.

Browser view of a Rear-Half-Vehicle Model Systems and Subsystems Employing a Quad-link Suspension
| • | Front MacPherson Strut (1pc LCA) |
| • | Front Multi-Link |
| • | Rear Trailing Arm Suspension |
| • | Rear Multi-Link (2 lower links) |