In this tutorial, you will learn how to:
| • | Mesh the clip, review the mesh quality, and determine the features to be simplified |
This exercise involves changing the shape of a part in order to simplify the geometry. Certain details of the shape, such as small holes or blends, may simply not be necessary for the analysis being performed. When these details are removed, the analysis can run more efficiently. Additionally, mesh quality is often improved as well. Changing the geometry to match the desired shape can also allow a mesh to be created more quickly.
Model Files
This exercise uses the clip_defeature.hm file, which can be found in the hm.zip file. Copy the file(s) from this directory to your working directory. This model file contains geometry that has been midsurfaced. Surfaces have been created on the mid-plane of the part.
Exercise
In this exercise, you will mesh the model using an element size of 2.5. You can assume a simple structural analysis will be run on the part, and thus does not require much detail. There are unnecessary features in this model that can also be removed.
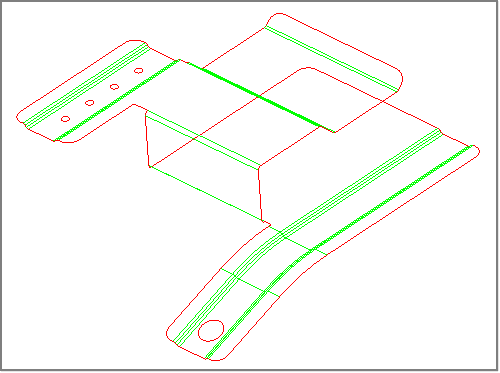
Step 1: Open and view the model file, clip_defeature.hm.
| 1. | From the menu bar, click File > Open > Model. |
| 2. | In the Open Model dialog, open the clip_defeature.hm model file. |
Step 2: To easily work with the midsurface, turn off the display of the lvl10 component.
If the lvl10 component is displayed, it needs to be turned off so that you can easily work on the midsurface geometry.
| 1. | In the Model browser, Component folder, click  next to lvl10 to turn off its geometry display. next to lvl10 to turn off its geometry display. |
Step 3: Mesh the clip to view mesh quality before defeaturing.
| 1. | To shade the model's geometry and surface edges, click 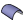 on the Visualization toolbar. on the Visualization toolbar. |
| 2. | To open the AutoMesh panel, click Mesh > Create > 2D AutoMesh from the menu bar, or press F12. |
| 3. | Set the entity selector to surfs. |
| 4. | In the element size = field, type 2.5. |
| 5. | From the mesh type list, select mixed. |
| 6. | Toggle the meshing mode from interactive to automatic. |
| 7. | Verify that the elems to surf comp toggle is set. |
| 8. | To select all of the displayed surfaces, click surfs >> displayed. |
| 9. | Click mesh. HyperMesh generates the mesh preview. |
Initial mesh on the clip model
| 10. | To exit the panel, click return. |
Step 4 (Optional): Review the quality of the mesh.
In this step, you will review the quality of the mesh that was created. Pay attention to the areas that have an irregular, poor quality mesh. An irregular, poor quality mesh generally contains rows and columns of quads that are not neat. You will use the Check Elements panel to evaluate the minimum length check of the elements.
| 1. | To open the Check Elements panel, click Mesh > Check > Elements > Check Elements from the menu bar, or press F10. |
| 2. | Go to the 2-d subpanel. |
| 3. | In the length < field, enter 1. |
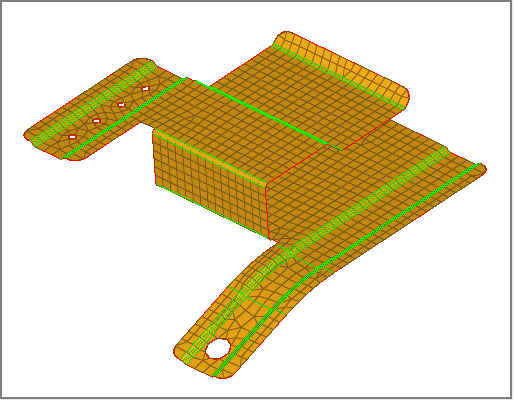
| 4. | To evaluate the minimum length, click length. Many of the elements that failed the length test are located around the fillets of this model. |
| Tip: | For better visualization of element quality, you may need to display the geometry in wire frame mode by clicking  on the Visualization toolbar. on the Visualization toolbar. |
Elements failing the length check
| 5. | To exit the panel, click return. |
Step 5: Remove the four small pinholes.
Pinholes are closed free edge loops within a surface. Pinholes do not need to be circular.
| 1. | To open the Defeature panel, click Geometry > Defeature > Pinholes from the menu bar. |
| 2. | In the diameter < field, enter 3.0. |
| 4. | Click find. HyperMesh identifies all of the pinholes that have a diameter of 3 or less in the model, and places a white xP symbol in their centers. |
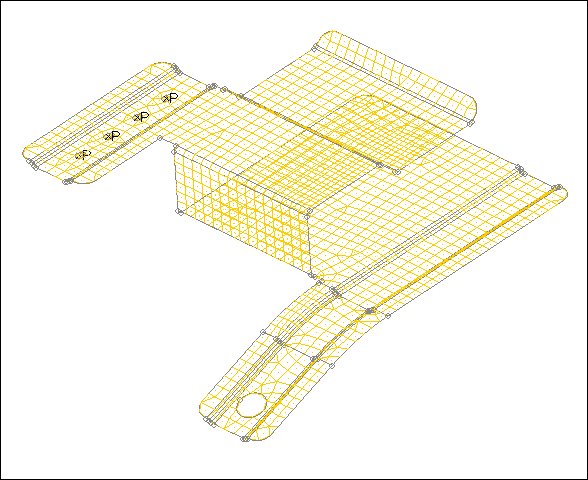
Pinholes identified using a 3 mm diameter
| 5. | Click delete. HyperMesh removes the selected pinholes in the model and replaces them with fixed points located at the center of the original pinholes. The mesh also updates according to the changes in the geometry. |
Step 6: Remove all surface fillets in the clip.
| 1. | Go to the surf fillets subpanel. |
| 2. | If the model's geometry and surface edges are not shaded, click  on the Visualization toolbar. on the Visualization toolbar. |
| 3. | Under find fillets in selected, click surfs >> displayed. |
| 4. | In the min radius field, type 2.0. |
| 5. | Click find. HyperMesh identifies all of the surface fillets with a radius of 2 or greater in the model. |
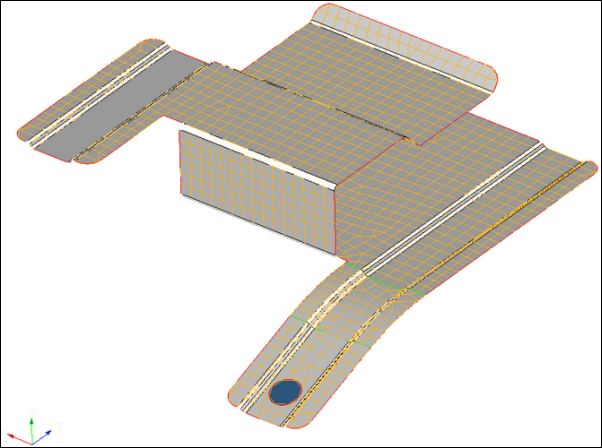
Surface fillets identified for removal
Step 7: Automatically identify and remove rounded corners of surfaces.
You should still be in the Defeature panel.
| 1. | Go to the edge fillets subpanel. |
| 2. | Click surfs >> displayed. |
| 3. | In the min radius field, type 1.0. |
| 4. | To find all of the fillets in the model, set the bottom switch to all. |
| 5. | Click find. HyperMesh identifies all of the edge fillets that meet the filter criteria, and displays a F symbol where they are located in the model along with radial lines. |
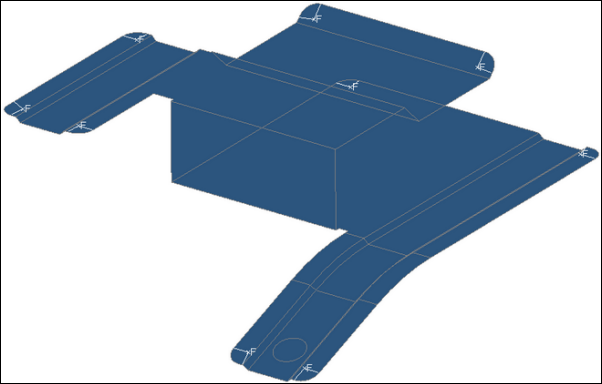
Edge fillets identified for removal
| 6. | With the fillets entity selector active, right-click on one of the F fillet markers on the screen to deselect the fillet. |
| 7. | Click remove. HyperMesh deletes all of the selected edge fillets except for the one which was deselected in step 6. |
Step 8 (Optional): Save your work.
Now that the model has been simplified, it is a good time to save the model.
| 1. | From the menu bar, click File > Save > Model. |
Summary
The model is now represented in a much simpler form that suits the analysis that will be performed. Holes, surface fillets, and edge fillets were removed that were considered too small to be captured by the desired element size of 2.5.
See Also:
HyperMesh Tutorials













