Eigenvalue Maximization with Topography Optimization |

|

|

|

|
|
Eigenvalue Maximization with Topography Optimization |

|

|

|

|
Eigenvalue Maximization with Topography Optimization |

|

|

|

|
|
Eigenvalue Maximization with Topography Optimization |

|

|

|

|
In this example, an irregularly shaped plate is optimized to increase its natural frequencies. The plate is supported at ten bolt locations around its perimeter. The edge of the plate is turned downward to add stiffness.
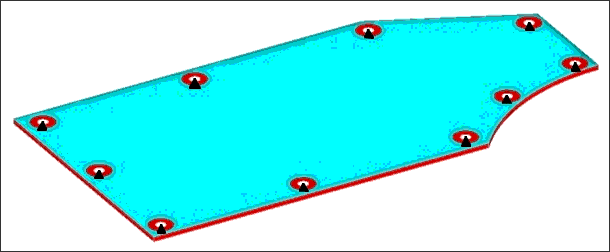
Cover plate model with constraints shown.
The red areas are excluded from the design domain. The blue area is open for OptiStruct to add a bead reinforcement pattern. The bead is drawn upward with respect to the plate orientation. The DTPG card used is as follows. Four different runs were made using different values for the draw height. The first run was made with a draw height of 20mm, the second with 40mm, the third with 60mm, and the fourth with 80mm.
(1) |
(2) |
(3) |
(4) |
(5) |
(6) |
(7) |
(8) |
(9) |
(10) |
DTPG |
1 |
PSHELL |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
20.0 |
60.0 |
YES |
65.0 |
NORM |
|
|
NONE |
|
The optimization is set up to maximize the frequencies of the first six modes (minimizing the sum of the weighted inverse eigenvalues) and to ensure that the first three modes were above certain design constraints. This is accomplished by placing the following cards in the subcase definition:
DESOBJ(MIN) |
1 |
DESSUB |
101 |
The following cards are placed in the bulk data section:
DRESP1 |
11 |
freq1 |
FREQ |
|
|
1 |
|
DRESP1 |
12 |
freq2 |
FREQ |
|
|
2 |
|
DRESP1 |
13 |
freq3 |
FREQ |
|
|
3 |
|
DRESP1 |
1 |
wfreq |
WFREQ |
|
|
|
|
DCONSTR |
101 |
11 |
400.0 |
|
|
|
|
DCONSTR |
101 |
12 |
500.0 |
|
|
|
|
DCONSTR |
101 |
13 |
600.0 |
|
|
|
|
DRESP2 |
1 |
wfreq |
900 |
|
|
|
|
Setting constraints on the first three modes results in separations between the frequency values of the modes and prevents OptiStruct from falling into local minimums when optimizing the modes. This approach ensures that a minimum performance criterion is satisfied. Note that for the 40mm, 60mm, and 80mm draw height runs, the constrained frequencies are higher than those shown above.
The solutions generated for the plate runs are shown in the following figures:
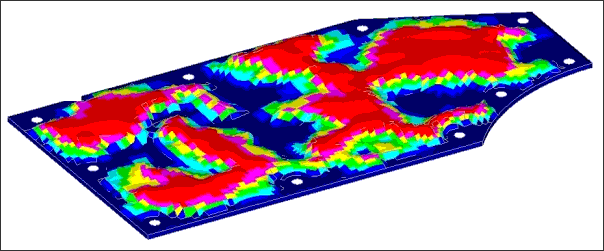
Solution for plate with draw height equal to 20mm.
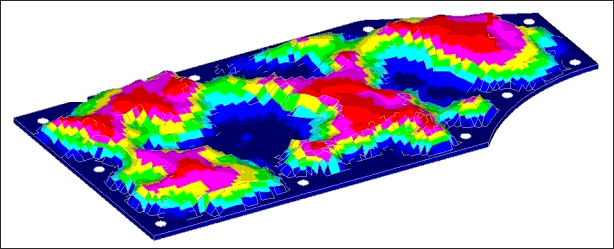
Solution for plate with draw height equal to 40mm.
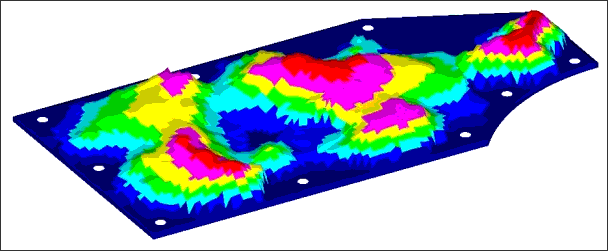
Solution for plate with draw height equal to 60mm.
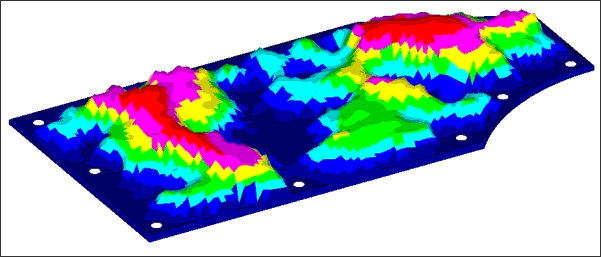
Solution for plate with draw height equal to 80mm.
The reinforcement patterns have a similar shape, but runs with a higher maximum draw height use more levels of draws throughout the plate. All of the solutions made good engineering sense, connecting the weak areas of the plate with beads running primarily across the short span of the plate. These beads were fluidly connected together across the long span of the plate allowing the beads to reinforce each other.
For the input file sample, see <install_directory>/demos/hwsolvers/optistruct/eigenplate.fem.
See Also: