Definition
Interface type 16 allows defining contact conditions between a group of nodes (slaves) and a curve surface of quadratic elements (master part), as shown in Fig. 5.34 for a symmetric contact. The master part may be made of 16-node thick shells or 20-node bricks. The Lagrange Multiplier method is used to apply the contact conditions; therefore, no gap is necessary to be applied. Some applications of this interface are sliding contacts without gaps as in gear box modeling.
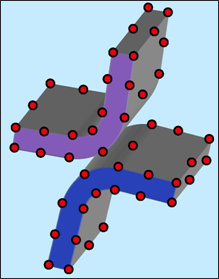
Fig. 5.34: Interface type 16 – node to quadratic surface contact
Interface type 17 allows modeling contact between two quadratic surfaces using the Lagrange Multiplier method. It is a generalized form of interface type 16 in which the contact on the two quadratic surfaces are directly resolved. The contact is supposed to be sliding or tied.
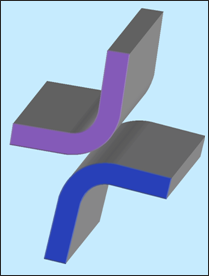
Fig. 5.35: Interface type 17 - quadratic surface to quadratic surface contact
As defined above, both interfaces do not model friction effects. Contact is either considered as tied or without friction (pure sliding).
| Note: | When using interfaces with the Lagrange Multiplier method, it is not recommended to symmetrize the contact. |
|