Spring (/PROP/SPRING) |

|

|

|

|
|
Spring (/PROP/SPRING) |

|

|

|

|
Spring type 4 is a simple physical spring, physical dashpot or parallel spring and dashpot. Time step depends on spring mass, stiffness and damping.
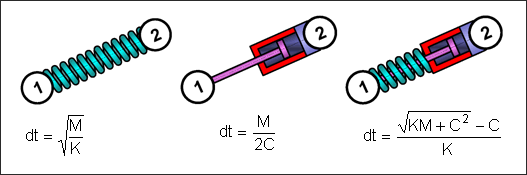
Fig. 3.1: Spring type 4 – time step
Critical spring time step ensures the stability of explicit time integration scheme, but it does not ensure a high accuracy on spring vibration behavior. Only two time steps are available during one vibration period of a free spring. To reproduce the true sinusoidal behavior, reduce the time step by a factor of at least 5. If the spring is used to connect two parts together, the spring vibration period increases and the default spring time step ensures stability and accuracy.
Spring type 4 has only one degree of freedom, it can only resist to axial traction and axial compression. The forces applied on the two nodes are always co-linear with direction 1-2.
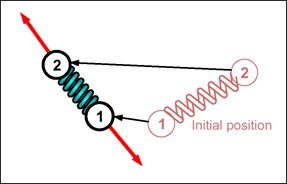
Fig. 3.2: Co-linear forces in spring type 4
If the spring works under compression, it can reach a zero length situation in which the orientation of internal forces can be arbitrary (Fig. 3.3). That can result in stability problems and should be avoided.
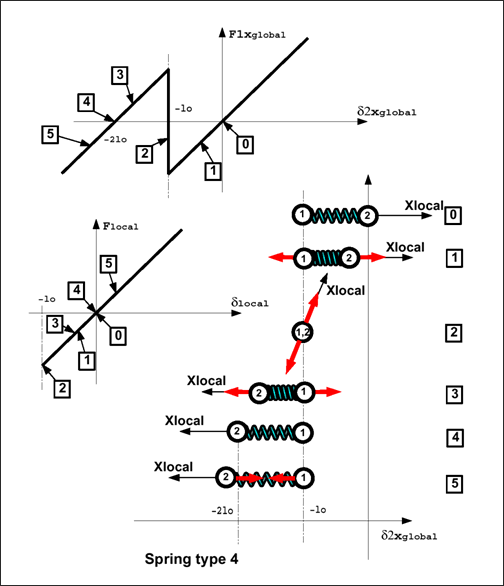
Fig. 3.3: Instability of a zero length spring
For further information, refer to the RADIOSS Theory Manual.