Panel Inputs
Input
|
Action
|
(entity selector)
|
Use the switch to choose the entities to apply the force to: nodes, points, sets or comps.
In any case, the moments are applied to nodes; this selection simply determines how those nodes are selected. Geometric points select the nodes at which they exist. Comps select all of the nodes contained within the chosen component.
If you choose comps or sets, Engineering Solutions draws the moments using a single indicator. As a result, a new button called display appears. This allows you to indicate where in the model you wish the indicator to be drawn, and requires additional steps.
When nodes is selected, use the switch to change the selection mode.
nodes
Select individual nodes.
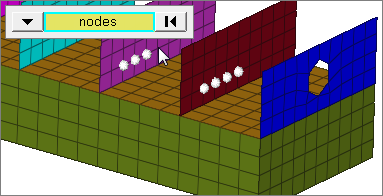
faces
Select all of the nodes on 2D and 3D faces.
If there are discontinuities on a 2D face, then only the nodes inbetween the discontinuities will be selected.
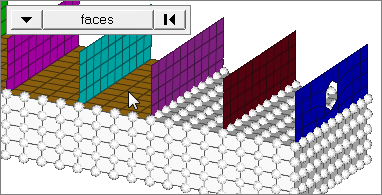
2D faces ext
Select all of the nodes on a 2D face that contain discontinuities.
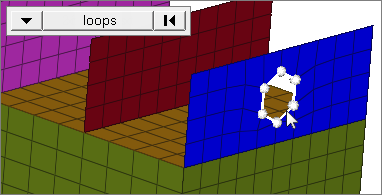
loops
Select all of the nodes on continuous free edges that make a closed loop simultaneously, such as the perimeter of a hole.
Only valid for SHELL elements.
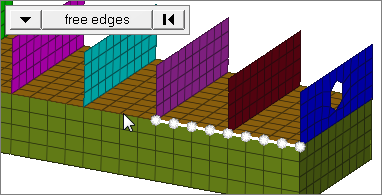
free edges
Select all of the nodes on free edges of elements.
If there are discontinuities on an edge, then only the nodes on the free edges inbetween the discontinuities will be selected.
Only valid for SHELL elements.
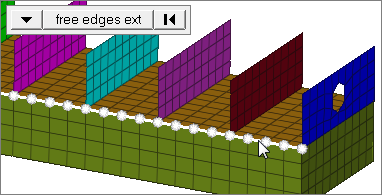
free edges ext
Select all of the nodes on free edges of elements that contain discontinuities.
Only valid for SHELL elements.
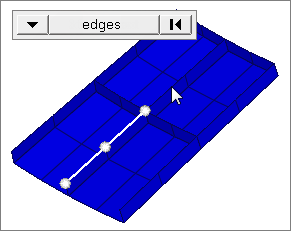
edges
Select all of the nodes on free edges or shared edges (butt joints, L/corner joints, and T-joints) of elements.
If there are discontinuities on an edge, then only the nodes on the edge inbetween the discontinuities will be selected.
Only valid for SHELL elements.
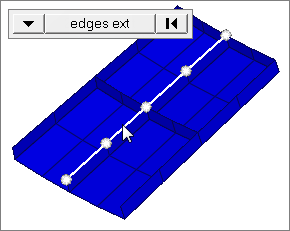
edges ext
Select all of the nodes on free edges or shared edges (butt joints, L/corner joints, and T-joints) of elements that contain discontinuities.
Only valid for SHELL elements.
|
global system / local system
|
Create the forces in the global system or the local system. If you select local system, enter the ID of the desired system.
|
magnitude / vector selector
|
Specify the magnitude and direction of the force in one of several ways. Each method is chosen from the upper of two adjacent switches.
| • | If you want to use the constant vector magnitude method, type in a magnitude, then use the plane and vector selector to specify the vector along which the force should act. |
| • | To specify the direction and magnitude of the force by typing in the force constant components, type in the x, y, and z values of the components. |
| • | If you select the curve, vector option (for moments that are time-dependent), specify a magnitude (y-scale) for the curve. Next, click the curve field twice to select from a list and then use the plane and vector selector to specify a direction, if necessary. Finally, specify a factor for the curve’s xscale. This allows you to use the same curve for many different cases, but vary the scale of its intensity or time to match the needs of your current moment. |
| • | If you choose the curve, components option, type in the X, Y, and Z components to define the direction and magnitude--for example, (2,2,2) will be twice the magnitude of (1,1,1). Next, click the curve field twice to select from a list. Finally, specify a factor for the curve’s xscale. This allows you to use the same curve for many different cases, but vary the scale of its intensity or time to match the needs of your current moment. |
Equations allow you to create force, moment, pressure, temperature or flux loads on your model where the magnitude of the load is a function of the coordinates of the entity to which it is applied. An example of such a load might be an applied temperature whose intensity dissipates as a function of distance from the application point, or a pressure on a container walls due to the level of a fluid inside.
Functions must be of the form magnitude= f(x,y,z). The only variables allowed are x, y and z, (lower case) which are substituted with the coordinate values of the entity to which the load is applied. In the case of grid point loads (force, moment or temperature) the grid point coordinates are used. For elemental loads (pressure or flux) the element centroid coordinates are used. In the event that a cylindrical or spherical coordinate system is used, x, y and z are still used to reference the corresponding direction. Standard mathematical operators and functions can be used; however, any functions requiring external data will not be valid. See Functions and Operators for a complete list.
| Note: | If your equation contains a syntax error, no warning message will be displayed, but any loads created will have a zero magnitude. |
Examples:
A flat plate, 20 x 20 units, lying in the X-Y plane with the origin at the center. A linear function for an applied force
magnitude = 20 – (5*x+2*y):
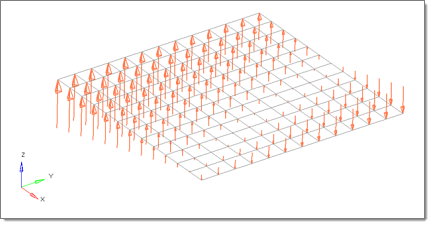
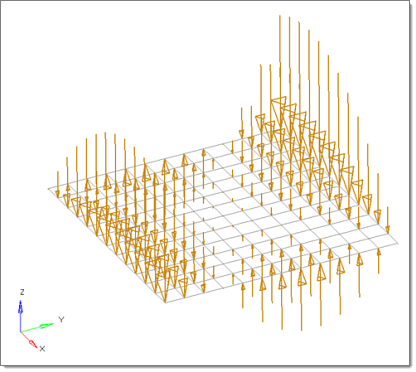
The same plate with a polynomial function
magnitude = x^2-2y^2+x*y+x+y:
A curved surface with a polynomial function for an applied pressure magnitude = -((x^2+2*y^2+z)/1000). The pressure function is defined in terms of the cylindrical coordinate system displayed at the top edge of the elements.
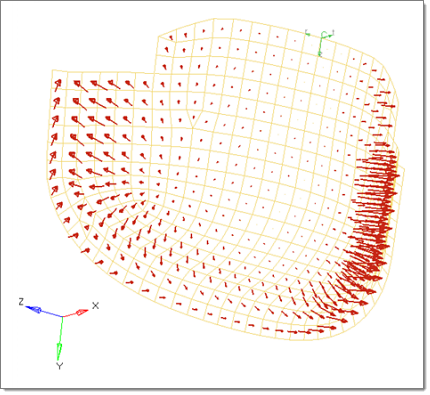
|
Optionally, you can also use the plane and vector selector to specify a direction, and select the coordinate system to which the vector corresponds.
| • | To interpolate forces from a saved file or existing loads, select linear interpolation (linear interpolation only works with shell elements). Each row of the input file contains the x,y, and z coordinates of the force followed by its 3-components. The data can be separated by a space or tab. |
You can then select the desired nodes to which you wish to add loads, and pick 3 or more existing loads that enclose those nodes. When you interpolate, a linear function is used to create additional loads on the selected nodes, with magnitudes based on the magnitudes of the loads that you had selected:
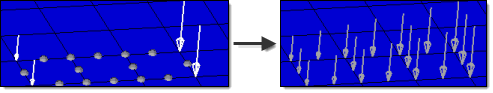
The search radius is a search distance to find the loads which are within that distance from a centroid or node on which a load is being interpolated. The nearest 3 loads located within that distance are used to create the load at the centroid or node by linear interpolation. Linear interpolation uses a triangulation method, so if it finds fewer than 3 loads within that distance no interpolation takes place. While reading the initial loads from a file, if linear interpolation is not possible because the search radius is too small, the original loads are simply applied to the nearest centroid or node.
| • | To interpolate and extrapolate forces from existing loads, select field loads. You can then select the desired elements to which you wish to add loads, and any existing loads on which you wish to base additional forces. |
When you create, <%HYPERMESH%> uses a Green’s function with the given boundary loads in order to create the loads on all of the selected nodes. For smoothness, the gradient at the boundary points is enforced to be zero; this ensures that the extrapolated loads remain lower than the input loads. For this reason it is recommended to use representative boundary values as input to be able to capture the peaks reasonably..
| Note: | This version differs from linear interpolation both in the way that the load magnitudes are determined, and also in the fact that it can be applied to nodes outside the boundaries of the chosen existing loads. |
| • | fill gap: When "fill gap" is checked, a load is created at every selected element centroid or node irrespective of the size of the search radius. |
|
relative size / size
|
relative size = display moments in a size relative to the model size (default 100).
size = display all moments with the same size.
|
label loads
|
Loads will include text labels that show the value of the moment.
|
load types
|
Select the desired load type; the options available depend on the current solver profile.
|
face angle / individual selection
|
Face angle
Value used to determine which of the selected elements are to have moments applied. For moments applied to faces, once the starting face has been identified, the normals of the adjacent remaining faces are tested. If the angle between the normals is less than the face angle, a moment is applied to the adjacent element. This process continues until all of the free faces have been tested. For a moment applied to edges, the process is similar except that the angle between edges is used instead of the angle between faces.
Only available when the entity selector is set to nodes and the selection mode is set to faces, 2d faces ext, free edges, free edges ext, edges, or edges ext.
Individual Selection
Select individual elements on a face or select individual free/shared edges of elements.
Only available when the entity selector is set to nodes and the selection mode is set to faces, free edges, or edges.
|
edge angle
|
Splits edges that belong to a given face.
When the edge angle is 180 degrees, edges are the continuous boundaries of faces. For smaller values, these same boundary edges are split wherever the angle between segments exceeds the specified value. A segment is the edge of a single element.
Only available when the entity selector is set to nodes and the selection mode is set to free edges, free edges ext, edges, or edges ext.
|
Comments
Loads from files formatted as CSV (Comma Separated Values) or SSV (Space-Separated Values) text files can be interpolated.
Field Loads will not overwrite any existing loads, so you can create an area of loads via linear interpolation and then use field loads to expand the load area without changing the loads already inside of the area.
|







