Before you begin this tutorial, it is recommended that you complete HM-1000: Getting Started with HyperMesh and Exploring the ANSYS Interface.
In this tutorial you will learn how to set up edge to edge contacts. In HyperMesh, you can create contact pairs manually or with the Autocontact tool. In this exercise you will learn how to set up contacts manually. You will create edge to edge contacts between circular and rectangular parts of the model. The edge of the circular body acts as a Target (slave) surface, and the top edge of the rectangular part acts as a contact (master) surface.
The steps mentioned in this tutorial are only applicable for HyperMesh 14.0.130 and on.
Model Files
This exercise uses the hm-ansys_contact_manager_2-d_tutorial.hm file, which can be found in <hm.zip>/interfaces/ansys/. Copy the file(s) from this directory to your working directory.
Exercise
Step 1: Load the ANSYS User Profile
| 1. | Start HyperMesh Desktop. |
| 2. | In the User Profile dialog, set the user profile to Ansys. |
Step 2: Retrieve the Model File
| 1. | From the menu bar, click File > Open > Model. |
| 2. | In the Open Model dialog, open the hm-ansys_contact_manager_2-d_tutorial.hm file. A model loads in the graphics area. |
| 3. | If the load collector is displayed, in the Model browser, click  next to the load collector to turn off the display of its element. next to the load collector to turn off the display of its element. |
| 4. | In the graphics area, click once to make it the current window for keyboard commands. |
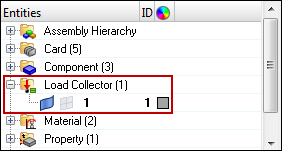
| 5. | Fit the model to the graphics area by pressing f. |
Step 3: Open the Contact Browser
| 1. | From the menu bar, click View > Browsers > HyperMesh > Contact. |
Step 4: Create Target (Slave) Surface
| 1. | In the first pane of the Contact browser, right-click and select Create > Contact Surfaces from the context menu. HyperMesh creates and opens a contact surface in the Entity Editor. |
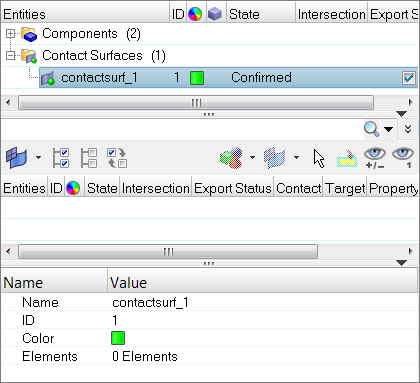
| 2. | In the Entity Editor, enter a name and ID, and select a color for the contact surface. |
| 3. | For Elements, click 0 Elements >> Elements. |
| 4. | In the panel area, set the first selector to add shell edges. |
| 5. | Select reverse normals. |
| 6. | For face angle, enter 30.0. |
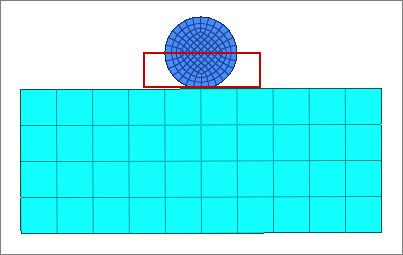
| 7. | Set the entity selector to elems, then select the free edges indicated in the image below. |
| Tip: | Quickly select elements with window selection by pressing SHIFT while clicking and dragging your mouse. |
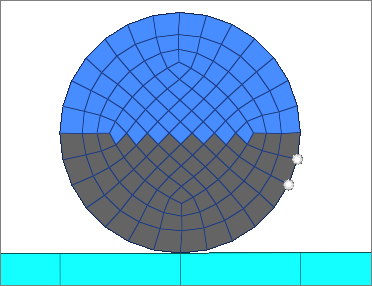
| 8. | Using the nodes selector, select two nodes along the free edges you have selected to identify the edge on which contact surface are to be created. |
| 9. | Click Add. All of the edges of the selected elements are added to the surface. |
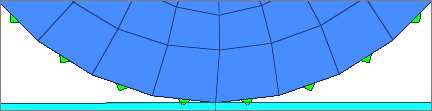
| 10. | Click return to exit the panel. |
| 11. | Review the contact surface you just created. |
| a. | In the Contact browser, right-click on contactsurf_1 and select Review from the context menu. |
| b. | Isolate the contact surface for a better visual display. The surface created here will be considered the target (slave) surface during analysis. |
Step 5: Create Contact (Master) Surface
| 1. | In the first pane of the Contact browser, right-click and select Create > Contact Surfaces from the context menu. HyperMesh creates and opens a contact surface in the Entity Editor. |
| 2. | In the Entity Editor, enter a name and ID, and select a color for the contact surface. |
| 3. | For Elements, click 0 Elements >> Elements. |
| 4. | In the panel area, set the first selector to add shell edges. |
| 5. | For face angle, enter 30.0. |
| 6. | Select reverse normals. |
| 7. | Set the entity selector to free edges, then select the top free edges of the rectangular box as indicates in the image below. |
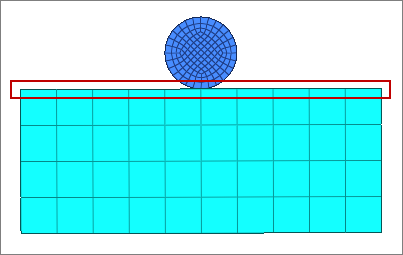
| 8. | Click add. Surfaces are created on the top edge of the rectangular box. |
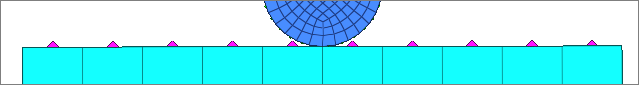
| 9. | Click return to exit the panel. |
Step 6: Create a Contact Pair
| 1. | In the second pane of the Contact browser, right-click and select Create > Contact Pair from the context menu. HyperMesh creates and opens a contact pair in the Entity Editor. |
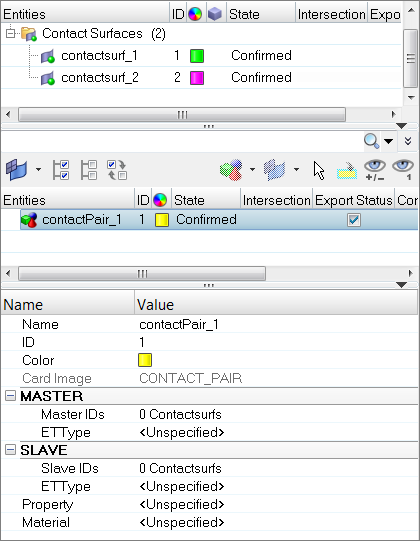
| 2. | In the Entity Editor, enter a name and ID, and select a color for the contact pair. |
| 3. | Attach the contact (master) surface. |
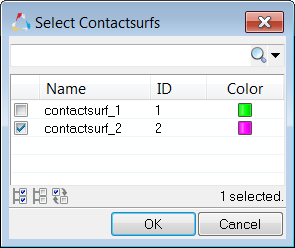
| a. | For Master IDs, click 0 Contactsurfs >> Contactsurfs. |
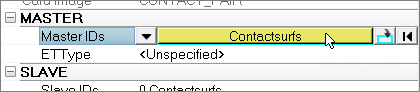
| b. | In the Select Contactsurfs dialog, select contactsurf_2 and click OK. |
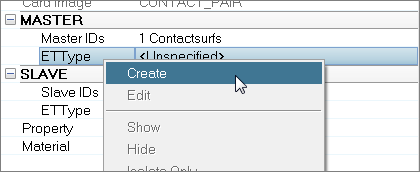
| c. | Under MASTER, right-click on ETType, and select Create from the context menu. |
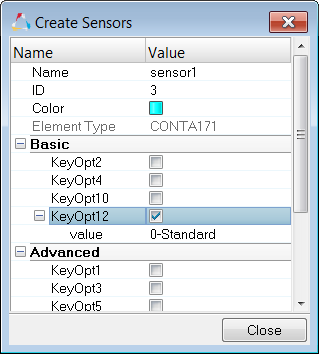
| d. | In the Create Sensors dialog, define the sensor and click Close. |
| • | By default, the Element Type is set to CONTA171. |
| • | Enable KeyOpt12, then select 0-Standard from the list. Keyopts determine the behavior of contacts during analysis. KeyOpt12 defines the type of contact. |
| 4. | Attach the target (slave) surface. |
| a. | For Slave IDs, click 0 Contactsurfs >> Contactsurfs. |
| b. | In the Select Contactsurfs dialog, select contactsurf_1 and click OK. |
In this contact pair, contactsurf_1 acts as the target (slave) surface. This surface will be exported with the element type Targe169.
| c. | Under SLAVE, right-click on ETType and select Create from the context menu. |
| d. | In the Create Sensors dialog, define the sensor and click Close. |
| • | By default, the Element Type is set to Targe169. |
| • | Enable KeyOpt4, then select 111-ROTZ, UY, UX from the list. |
The target (slave) surface will be exported with the elements type TARGE169.
| 5. | Create and attach the contact property. |
A contact property for a pair is always required, as the solver recognizes the pair only by the property ID associated with the master and slave surfaces. Same property IDs are shared by the master and slave surfaces. If a property ID is missing for a contact surface, then it will not considered as part of the contact pair and it will not recognized.
| a. | In the Entity Editor, right-click on Property and select Create from the context menu. |
| b. | In the Create Properties dialog, define the property and click Close. |
| 6. | Create and attach the contact material. |
The properties MU (coefficient of friction) and EMIS (Thermal Emissivity) are available to define. If you are creating a structural contact, select MU; if you are creating a thermal contact, select EMIS. In this exercise you will be creating a structural contact.
| a. | In the Entity Editor, right-click on Material and select Create from the context menu. |
| b. | In the Create Materials dialog, define the material and click Close. |
| • | Select the MU (coefficient of friction) checkbox. |
| • | Under MP_MU_LEN=, next to Data: C, click  . . |
| • | In the MP_MU_LEN= dialog, enter 0.45 and click Close. |
Step 7: Review the Contact Pair
| 1. | In the second pane of the Contact browser, select the contact pair to display its entity details in the Entity Editor. |
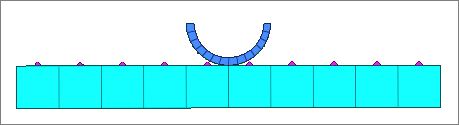
| 2. | Right-click on the contact pair and select Isolate Attached > Elements to review the contact area. |
Step 8 (Optional): Add /SOLU, ANTYPE, and SOLVE in the Control Cards
If your model needs to be solved in ANSYS, add the following control cards.
| 1. | Open the Control Cards panel by clicking Setup > Create > Control Cards from the menu bar. |
| 2. | Click /SOLU to exit the PREP7 preprocessor and enter the SOLU preprocessor. |

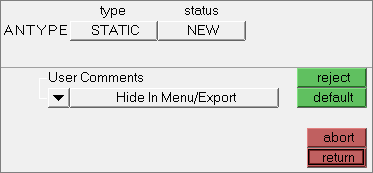
| 4. | Since you are solving the model for static analysis, click ANTYPE. |
| 5. | Set type to STATIC and status to NEW. |
| Note: | If you do not see the SOLVE control card, click next. |

| 8. | Click return to exit the card image. |
| 9. | Click return to exit the Control Cards panel. |
See Also:
HyperMesh Tutorials