In this tutorial, you will learn how to create a hexahedral mesh using the Solid map function by one volume and multisolid method.
Solids are geometric entities that define a three-dimensional volume. The use of solid geometry is helpful when dividing a part into multiple volumes. For example, divide a part into simple, mappable regions to hex mesh the part. Use the Solid Map panel to create a mesh of solid elements in a solid geometric volume.
Model Files
This exercise uses the solid_map.hm file, which can be found in the hm.zip file. Copy the file(s) from this directory to your working directory.
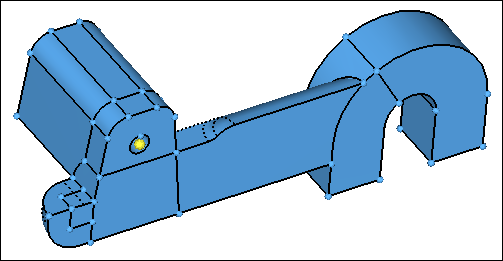
Exercise: Hex-meshing Solid Geometry
Step 1: Retrieve model file, solid_map.hm.
| 1. | Start HyperMesh Desktop. |
| 2. | From the menu bar, click File > Open > Model. |
| 3. | In the Open Model dialog, open the solid_map.hm model file. |
Step 2: Mesh the 1/8th sphere-shaped region.
| 1. | Shade the model's geometry and surface edges by clicking  on the Visualization toolbar. on the Visualization toolbar. |
| 2. | Open the Solid Map Mesh panel by clicking Mesh > Create > Solid Map Mesh from the menu bar. |
| 3. | Go to the one volume subpanel. |
| 4. | Under along parameters, enter 1 in the elem size= field. |
| 5. | Activate the volume to mesh: solid entity selector. |
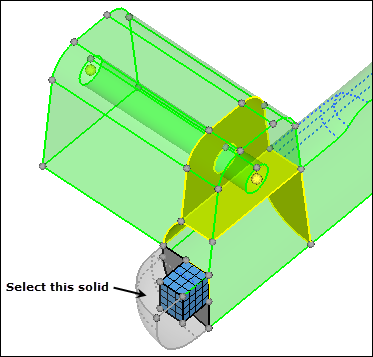
| 6. | Select the small cube-shaped solid, as indicated in the following image. |
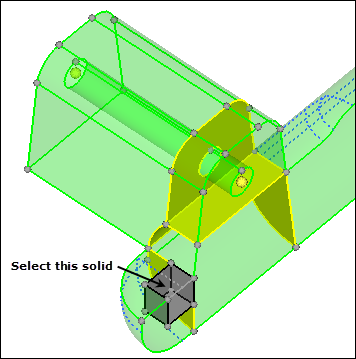
| 8. | Shade the model's elements and mesh lines by clicking  on the Visualization toolbar. on the Visualization toolbar. |
| 9. | Select the solid as indicated in the following image. |
| 11. | Return to the main menu by clicking return. |
Step 3: Create a shell mesh with the Automesh panel to control a mesh pattern.
| 1. | Open the Automesh panel by clicking Mesh > Create > 2D AutoMesh from the menu bar. |
| 2. | Go to the size and bias subpanel. |
| 3. | Select the surface as indicated in the following image. |
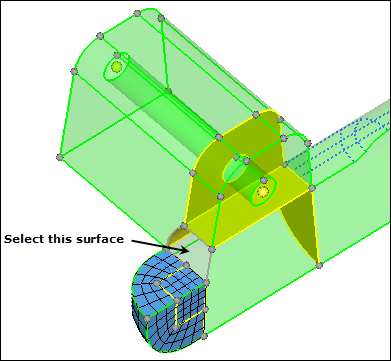
| 4. | Set the meshing mode to interactive. |
| 5. | In the element size = field, enter 1.000. |
| 6. | Set the mesh type to mixed. |
| 7. | Click mesh. The meshing module opens. |
| 8. | Verify that you are in the density subpanel. |
| 9. | In the elem density = field, enter 4. |
| 10. | Click set all to. HyperMesh sets all the edge densities to 4. |
| 12. | Return to the main menu by clicking return twice. |
Step 4: Mesh the solid volume on which the surface mesh was created in Step 3.
| 1. | Open the Solid Map Mesh panel. |
| 2. | Go to the one volume subpanel. |
| 3. | Select the volume shown in the following image. |
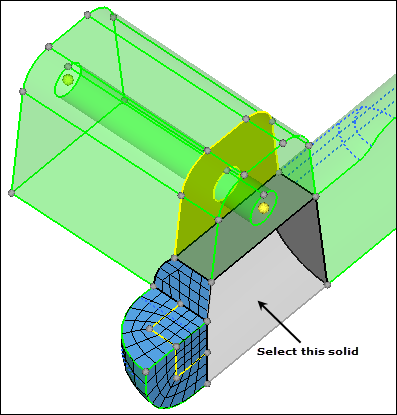
| 4. | Under along parameters, toggle elem size= to density= . |
| 5. | In the density= field, enter 10. |
| 7. | Rotate the part and note how the mesh pattern created with the Automesh panel has been used for the solid elements. |
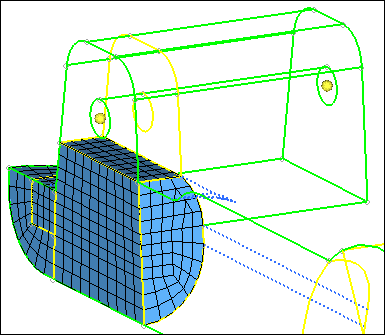
Step 5: Mesh the remaining solid volumes.
In this step, you should still be in the Solid Map Mesh panel, one volume subpanel.
| 1. | Select one of the remaining unmeshed solid volumes. |
| Note: | Make sure to select a solid adjacent to one that has already been meshed so that connectivity is maintained. |
| 2. | Set the source shells to mixed. |
| 3. | Under along parameters, toggle density= to elem size= |
| 4. | In the elem size= field, enter 1.5. |
| 6. | Repeat until all solid volumes are meshed. |
| 7. | Return to the main menu by clicking return. |
Step 6 (Optional): Save your work.
With this section of the exercise completed, it is a good time to save the model.
| 1. | From the menu bar, click File > Save > Model. |
Automated Solid Map Meshing
The capability to automate the solid map meshing process is now available. Using the “Mappable” visualization mode in conjunction with the multi-solids feature will inform you that the solid(s) are ready for solid meshing. Using the multi-solids feature will allow for all solids within the model to be meshed in one step, provided that they are mappable.
In this section of the tutorial, you will delete all of the elements from the previous section. You will then use the Mappable visualization mode with multi-solids to solid mesh the part.
Step 7: Delete the elements within the model.
| 1. | Open the Delete panel by pressing F2. |
| 4. | Return to the main menu by clicking return. |
Step 8: Use the mappable visualization mode.
| 1. | Shade the model's geometry and surface edges by clicking  on the Visualization toolbar. on the Visualization toolbar. |
| 2. | From the Geometry Visualization list, select  . HyperMesh color codes each solid to represent its mappable state. . HyperMesh color codes each solid to represent its mappable state. |
| Note: | The goal is to ensure that each solid is either 1-directional or 3-directional mappable. |
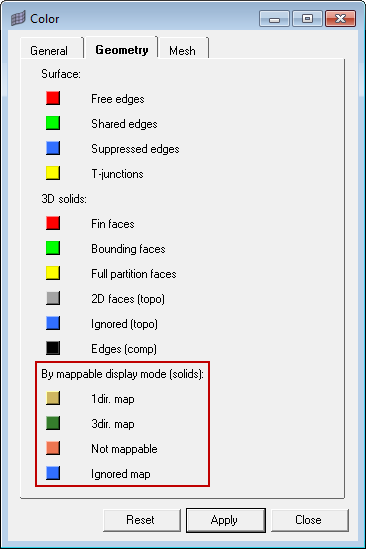
| 3. | From the menu bar, click Preferences > Colors. |
| 4. | In the Color dialog click the Geometry tab. |
| 5. | Optional: Under By mappable display mode (solids), click the color swatches to adjust the display color of the following: |
| • | 1dir. map: Visualization for solids that can be mapped, for 3D meshing, in one direction. |
| • | 3dir. map: Visualization for solids that can be mapped, for 3D meshing, in three directions. |
| • | ignored map: Default visualization for solids that require partitioning to become mappable. |
| • | not mappable: Visualization for solids that have been edited, but still require further partitioning to create mappable solids. |
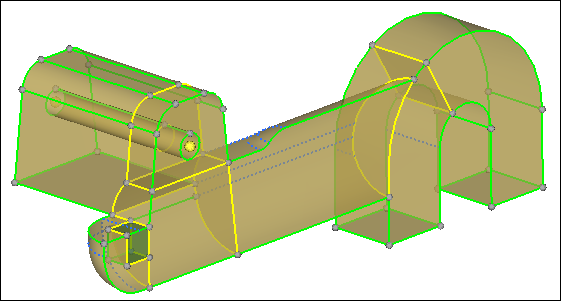
Once in the mappable visualization mode, it is clear that there is one 3-directional mappable solid and the rest are 1-directional mappable.
Step 9: Use the multi-solid feature to mesh the part.
| 1. | Open the Solid Map Mesh panel. |
| 2. | Go to the multi solids subpanel. |
| 3. | Click solids >> all. HyperMesh selects all of the solids in the model. |
| 4. | Set the source shells to mixed. |
| 5. | In the elem size field, enter 1. |
| 6. | Click mesh. HyperMesh opens the interactive mesh mode. |
| 7. | Accept the shell elements and create solid elements by clicking mesh. |
| Note: | The solids will be sequentially solid meshed. |
| 8. | Inspect the model and note that the mesh within all of the solids is correctly equivalenced. |
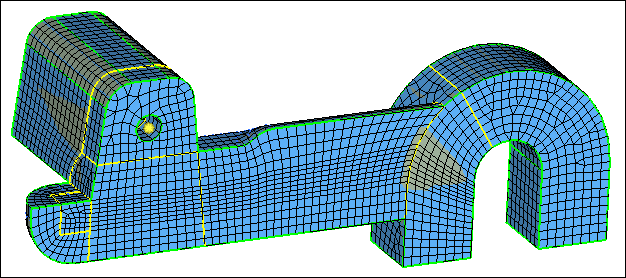
| 9. | Accept the solid element mesh and return to the Solid Map Mesh panel by clicking return. |
Step 10 (Optional): Save your work.
With this exercise completed, you can save the model if desired.
| 1. | From the menu bar, click File > Save > Model. |
See Also:
HyperMesh Tutorials