This tutorial demonstrates how to perform a multi-objective optimization with HyperStudy.
Before running this tutorial, you must complete HS-1035: Optimization Study Using an Excel Spreadsheet or you can import the archive file HS-1035.hstx, available in <hst.zip>/HS-4205/.
In the initial optimization problem, as stated in tutorial HS-1035, the objective is to find the cross-sectional dimensions (width and height) of a beam that minimize the beam volume while keeping the tip deflection below 0.53 mm.
In this tutorial, both the beam volume and tip deflection will be considered as objective functions to be minimized. The constraint in the tip deflection is not applied in an effort to understand the trade-off associated with this condition. Using a Global Response Surface Method (GRSM), a series of solutions (called non-dominated solutions), will be found. These solutions form a Pareto front in which users can do trade-off analysis.
| 2. | Perform all steps in tutorial HS-1035. |
|
| 1. | In the Explorer, right-click and select Add Approach from the context menu. |
| 2. | In the HyperStudy - Add dialog, select Optimization and click OK. |
| 3. | Go to the Select Input Variables step. |
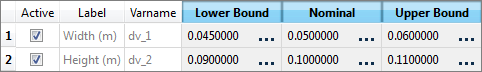
| 4. | For both input variables, change the lower, initial, and upper bounds to the values indicated in the image below. |
| 5. | Go to the Select Output Responses step. |
| a. | Click the Objectives tab. |
| c. | In the HyperStudy - Add dialog, add two objectives. |
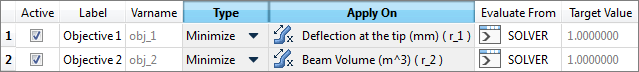
| d. | Define Objective 1 and Objective 2 by selecting the options indicated in the image below from the Type and Apply On columns. |
| 8. | Go to the Specifications step. |
| 9. | In the work area, set the Mode to Global Response Surface Method (GRSM). |
| Note: | Only the methods that are valid for the problem formulation are enabled. |
| 11. | Go to the Evaluate step. |
| 12. | Click Evaluate Tasks to launch the Optimization. |
| 13. | Optional. HyperStudy also allows you to perform multi-objective Optimizations using a Weighted Sum approach. Add and activate multiple objectives amongst the output responses, set a weight respectively for each objective in the Weighted Sum field, and select an algorithm (SQP, MFD, GA, ARSM) in the Specifications table. Proceed with the optimization. |
| 14. | Go to the Post processing step. |
|
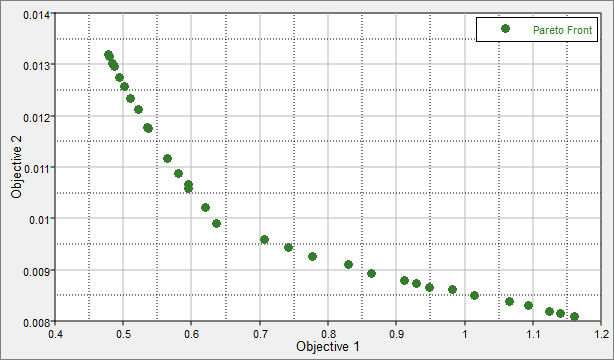
| 2. | Using the Channel selector, select Objective 1 for the X Axis and Objective 2 for the Y Axis. |
The Optima tab plots the trade-off between competing objectives. One objective cannot improve without the other competing objective getting worse.
|
See Also:
HyperStudy Tutorials