ACMODL |

|

|

|

|
|
ACMODL |

|

|

|

|
ACMODL – Fluid-Structure Interface Parameters
Defines model parameters for the fluid-structure interface.
(1) |
(2) |
(3) |
(4) |
(5) |
(6) |
(7) |
(8) |
(9) |
(10) |
ACMODL |
INTER |
INFOR |
FSET |
SSET |
NORMAL |
|
SKNEPS |
DSKNEPS |
|
|
INTOL |
|
SRCHUNIT |
MAXSGRID |
|
|
|
|
|
Field |
Contents |
INTER |
Fluid-structure interface type. Default = DIFF (IDENT or DIFF) |
INFOR |
Defines whether grids or elements identified by FSET and SSET are to be used to define the fluid-structure interface. Default = GRID (GRID or ELEMENT) |
FSET |
ID of a SET of fluid elements or grids to be considered for the interface. Default = blank (Integer) |
SSET |
ID of a SET of structural elements or grids to be considered for the interface Default = blank (Integer) |
NORMAL |
Fluid normal tolerance. Default = 1.0 when INTER = DIFF; |
SKNEPS |
Fluid skin growth tolerance (Comments 4 and 5). Default = 0.5 (Real) |
DSKNEPS |
Secondary fluid skin growth tolerance (Comments 4 and 5). Default = 1.5 * SKNEPS (Real) |
INTOL |
Tolerance of inward normal. Default = 0.5 (Real) |
SRCHUNIT |
Search units. ABS for absolute model units or REL for relative model units based on element size. Default = REL (ABS or REL) |
MAXSGRID |
The maximum number of structural grids that can be interfaced with one fluid element face. Default = 200 (Integer > 0) |
| 1. | ACMODL card is optional in the deck. If provided, only one ACMODL card is allowed. |
| 2. | For INTER=IDENT, the interface would be calculated based on a grid to grid match between fluid and structural parts. For INTER=IDENT, INFOR must be GRID or blank. Each grid specified on the FSET/SSET must be able to find a matching interface grid. If either FSET or SSET is not provided, a searching algorithm would find the grids on the skin of the surface. |
| 3. | For INTER=DIFF, if FSET/SSET is provided, the skin of the surface would be based on the set. If either FSET or SSET is not provided, a searching algorithm would find the skin of the surface. The searching algorithm for this case is based on the normal distance from the fluid face. When INTER=DIFF, a grid to grid match is no longer a requirement. |
| 4. | The search box is described by several parameters: |
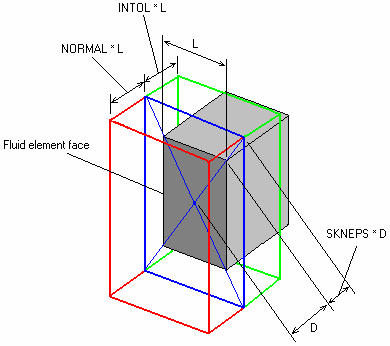
| • | The height of the searching box is based on the NORMAL parameter. If L is the smallest edge of the fluid element face, the height of the search box would be NORMAL x L. |
| • | SKNEPS represents the enlargement of the plane of the fluid surface used to define the search box. The diagonal distance, D, from the center of the fluid surface to each surface grid is pushed out by (1.0+SKNEPS) x D. |
| • | DSKNEPS represents a secondary enlargement of the plane of the fluid surface used to define the search box if SKNEPS fails to find ANY structural elements. The diagonal distance from the center of the fluid surface to each surface grid is pushed out by (1.0+DSKNEPS) x D. |
| • | INTOL represents a normal direction into the fluid for the case when the fluid protrudes past the structural interface. It is defined as INTOL x L, where L is the smallest edge of the fluid element surface. |
| 5. | The value required in the secondary fluid skin growth tolerance (DSKNEPS) field must always be greater than the value of the fluid growth tolerance (SKNEPS). |
| • | If the required value of DSKNEPS is less than SKNEPS, an ERROR message will be output and the run will be terminated. |
| • | If the DSKNEPS field is left blank, a default value equal to 1.5 * SKNEPS is assigned to it. |
| 6. | This card is represented as a control card in HyperMesh. |
See Also:
Coupled Frequency Response Analysis of Fluid-Structure Models