DEQATN |

|

|

|

|
|
DEQATN |

|

|

|

|
Bulk Data Entry
DEQATN – Design Equation Definition
Description
Specifies one or more equations for use in optimization.
Format
(1) |
(2) |
(3) |
(4) |
(5) |
(6) |
(7) |
(8) |
(9) |
(10) |
DEQATN |
EQUID |
EQN1; |
EQN2; |
EQN3; |
|
||||
|
…; … ; EQNn-1; EQNn |
|
|||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||
Field |
Contents |
EQUID |
Unique equation identification number. (Integer > 0) |
EQNi |
i-th equation. (Character string) |
| 1. | Each equation card is specified in a fixed format, without the limitation of data field boundaries. Equations are located in columns 17-72 on the first card, and in columns 9-72 on each continuation card. There is no limit on the total length of any equation. |
| 2. | Large field format is not allowed. |
| 3. | Free field format is allowed, but only the same number of characters as in the fixed format (56 on the first line and 64 on the continuation lines) and will be accepted. Characters after the 72nd column will not be accepted. Excess characters are silently disregarded, which may result in DEQATN error or in a valid expression different from that intended. On the continuation card in free format, the comma must be present within the first 8 columns; otherwise, the card will be interpreted in a fixed field format. |
| 4. | Blank characters in the equation have no effect, even within a constant, variable or function name. Lower and upper case letters are equivalent. |
| 5. | There must be only one variable at the left-hand side of each equation in any equation card. The variable of the first equation must be followed by an argument list in the following format: |
v1(x1,x2,…,xn) = expression(x1,x2,…,xn);
v2 = expression(x1,x2,…,xn,v1);
…
vi = expression(x1,x2,…,xn,v1,v2,…,vi-1);
…
vn = expression(x1,x2,…,xn,v1,v2,…,vn-1);
Where, vi is the variable of equation i. (x1, x2, …, xn) is the argument list for variable v1. (v1,v2,…,vi-1) is the variable list which corresponds to the result of equation 1 through equation i-1.
Only the value of the last expression is returned to the bulk data card referencing EQUID (DRESP2).
| 6. | Constants can be specified in a format of either integer or floating point. A floating point number can be in a format of either normal decimal-point format (3.90) or scientific notation (-2.0E-3), which means -2x10-3. |
The list of supported mathematical functions is as follows:
One-argument functions
abs(x) acos(x) acosh(x) asin(x) asinh(x) atan(x) atanh(x) cos(x) cosh(x) exp(x) log(x) log10(x) pi(x) sin(x) sinh(x) int (x) sqrt(x) |
absolute value arccosine hyperbolic arccosine arcsine hyperbolic arcsine arctangent hyperbolic arctangent cosine hyperbolic cosine exponential natural logarithm common logarithm multiples of sine hyperbolic sine real to integer conversion square root |
Two-argument functions
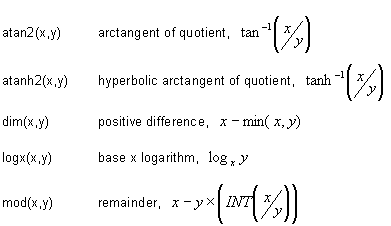
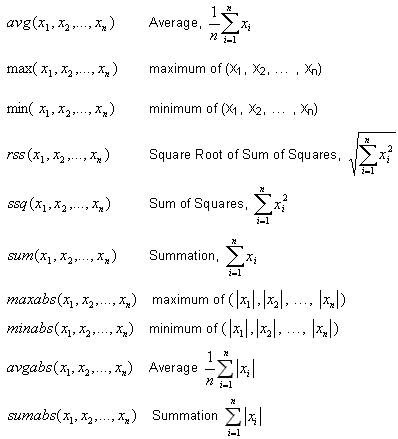
Multi-argument functions
| 7. | The supported operators are listed below: |
Symbol |
Meaning |
Example |
|---|---|---|
+ |
binary + |
x + y |
- |
binary - |
x - y |
* |
multiplication, |
x * y |
/ |
division |
x / y |
** |
power |
x**y |
+ |
unary + |
+1.0 |
- |
unary - |
-1.0 |
| 8. | The precedence of mathematical calculations follows the rules of Fortran language. Parenthesis has a higher priority in the order of precedence than the operators listed above. Two consecutive operators are acceptable only if the second one is unary, plus or minus. |
Examples of operator precedence:
Expression |
Result |
|---|---|
2**-3 |
0.128 |
1 / 2 + 3 |
3.5 |
2*3-4 |
2.0 |
-2**3**2 |
-512.0 |
2 + -5 |
-3.0 |
2 * -5 |
-10.0 |
2 - -5 |
7.0 |
2/3/4 |
0.16666666… |
2/(3/4) |
2.6666666… |
| 9. | Functions can be defined in a layered format, for example, min(sin(x1), x2), with no limit on the number of layers. |
DRESP2 card, the variable identified by DVIDi, LABj, NRk, Gr and DPIP correspond to variable arguments listed in the left-hand side of the first equation of a DEQATN card identified by EQUID. The variable arguments x1 through xN (where N = n + m + p + q + s) are assigned in the order DVID1, DVID2, …, DVIDn, LAB1, LAB2, …, LABm, NR1,NR2, …, NRp, G1, …, Gq, DPIP1,…,DPIPS. In a DVPREL2 card, the variables identified by DVIDi and LABj correspond to variable arguments listed in the left-hand side of the first equation of a DEQATN card identified by EQUID. The variable arguments x1 through xN (where N = n + m) are assigned in the order DVID1, DVID2, …, DVIDn, LAB1, LAB2, …, LABm.
Only the computed value of the last expression (vn) is used by DRESP2 and/or DVPREL2 entry.
| 11. | This card is represented as an optimizationfunction in HyperMesh. |
Restrictions
| • | Variable names longer than 8 characters are truncated, which may create an error in equation if two names are identical after such truncation. |
| • | All trigonometric arguments are in radians. |
| • | Only alphanumeric characters may be used in variable names (that is do not use underscores, monetary symbols, punctuation symbols, mathematical operators, letters from non-English alphabet, and so on). |
| • | Mathematical function names (such as those listed in comment 6 above) should not be used as variable names. |
| • | The following functions are not accepted: |
DB()
DBA()
INVDB()
INVDBA()
Possible Errors
An informative error message with the DEQATN ID will be displayed if the parsing of the equation fails. However, in certain cases, the following generic message will be provided:
Error 1690: |
This equation could not be parsed. See the DEQATN entry in the OptiStruct manual. |
This error message means that it was not possible to clearly identify the reason for the failure. If this happens, check for the following possible causes, and contact ossupport@altair.com:
| • | The length of the equation exceeds the 72 character per line limitation |
| • | The last character of the equation is an operator |
| • | There are two adjacent operators in the equation |
| • | There are non-alphanumeric characters (besides operators) in the equation |
See Also: