Example 14 - Truck with Flexible Body |

|

|

|

|
|
Example 14 - Truck with Flexible Body |

|

|

|

|
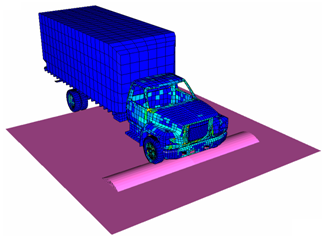
This example compares different studies with flexible or rigid bodies. The method for using the flexible bodies in an explicit analysis is also studied.
At first, the truck is modeled using a classical finite element model for explicit analysis. All parts of the truck are modeled using different kinds of finite elements, such as shells, bricks, springs and beams. The volumes monitored with perfect gas characterize the tires.
The problem is divided into two loading phases. First, gravity is applied as a quasi-static load. Then, the truck’s Virtual Proving Ground (VPG) is studied to observe the truck driving over an obstacle (bump).
For the gravity loading phase, the explicit approach using relaxation techniques or not is employed. For the VPG analysis, three approaches are compared: (i) classical finite element model; (ii) simplified finite element model with a global rigid body; and (iii) finite element model involving a flexible body. The last approach requires the first run to compute the Eigen and static modes. A flexible body input file is then generated for use in a second time-history run. The main interest of this method is to economize the CPU time.