MAT9ORT |

|

|

|

|
|
MAT9ORT |

|

|

|

|
Bulk Data Entry
MAT9ORT – Material Property Definition, Form 9-Orthotropic
Defines the material properties for linear, temperature-independent, and orthotropic materials for solid elements in terms of engineering constants.
Format
(1) |
(2) |
(3) |
(4) |
(5) |
(6) |
(7) |
(8) |
(9) |
(10) |
MAT9ORT |
MID |
E1 |
E2 |
E3 |
NU12 |
NU23 |
NU31 |
RHO |
|
|
G12 |
G23 |
G31 |
A1 |
A2 |
A3 |
TREF |
GE |
|
|
Field |
Contents |
|---|---|
MID |
Material identification number. Must be unique with respect to other MAT1, MAT2, MAT8, MAT9, and MAT9ORT definitions. No default (Integer > 0) |
E1 |
Elastic modulus in 1-direction. No default (Real) |
E2 |
Elastic modulus in 2-direction. No default (Real) |
E3 |
Elastic modulus in 3-direction. No default (Real) |
NU12 |
Poisson’s ratio for uniaxial loading in 1-direction. See comment 3. No default (Real) |
NU23 |
Poisson’s ratio for uniaxial loading in 2-direction. See comment 3. No default (Real) |
NU31 |
Poisson’s ratio for uniaxial loading in 3-direction. See comment 3. Default = NU23 (Real) |
RHO |
Mass density. No default (Real) |
G12 |
Shear modulus on plane 1-2. |
G23 |
Shear modulus on plane 2-3. |
G31 |
Shear modulus on plane 3-1. |
Ai |
Coefficient of thermal expansion in the i-direction Default =0.0 (Real) |
TREF |
Reference temperature for the calculation of thermal loads. Default = blank (Real or blank) |
GE |
Structural element damping coefficient. See comment 5. Default = 0.0 (Real) |
| 1. | This input definition is internally converted to an equivalent MAT9 definition on reading (Comment 6). This is reflected in echoed (ECHO) input data and all messaging. |
| 2. | The material identification number must be unique for all MAT1, MAT2, MAT8, MAT9 and MAT9ORT entries. |
| 3. | In general, |
Furthermore, material stability requires that:
![]() and
and ![]()
| 4. | It may be difficult to find all nine orthotropic constants. In some practical problems, the material properties may be reduced to normal anisotropy in which the material is isotropic in a plane (for example, plane 1-2), and has different properties in the direction normal to this plane. |
In the plane of isotropy, the properties are reduced to:
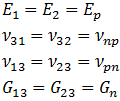
with ![]() and
and ![]()
There are five independent material constants for normal anisotropy (Ep, En, vp, vnp, and Gn).
In case the material has a planar anisotropy, in which the material is orthotropic only in a plane, the elastic constants are reduced to seven (E1, E2, E3, v12, G12, G23, and G31).
| 5. | To obtain the damping coefficient GE, multiply the critical damping ratio, C/C0 by 2.0. |
| 6. | Internal conversion from MAT9ORT to MAT9. The material property fields of the MAT9 entry are calculated internally from the MAT9ORT entry using the following formula: |
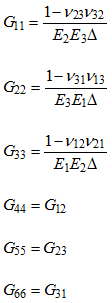
![]()
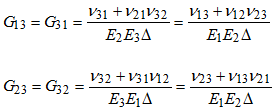
Where,
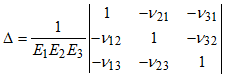
The values of ![]() , E and G for the expressions in the above equations in comment 7 are taken from the NUij , Ei and Gij fields respectively of this MAT9ORT entry where i, j € {1,2,3} and the values of G11, G22, G33, G44, G55, G66, G12, G13, and G23 (see above equations) are used to populate the G11, G22, G33, G44, G55, G66, G12, G13, and G23 fields (G12=G21, G13=G31 and G23=G32 due to symmetry) of the MAT9 entry. The remaining elements of the MAT9 entry (that is G14, G15, G24, and so on) are equal to zero.
, E and G for the expressions in the above equations in comment 7 are taken from the NUij , Ei and Gij fields respectively of this MAT9ORT entry where i, j € {1,2,3} and the values of G11, G22, G33, G44, G55, G66, G12, G13, and G23 (see above equations) are used to populate the G11, G22, G33, G44, G55, G66, G12, G13, and G23 fields (G12=G21, G13=G31 and G23=G32 due to symmetry) of the MAT9 entry. The remaining elements of the MAT9 entry (that is G14, G15, G24, and so on) are equal to zero.
See Also: