Materials |

|

|

|

|
|
Materials |

|

|

|

|
The Material Properties dialog allows you to view, add, and edit the material properties that are used for NLFE bodies.
MotionView provides a list of properties by default for commonly used materials.
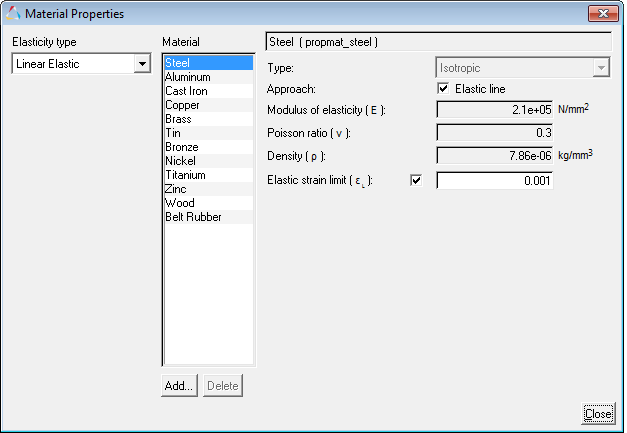
Material Properties dialog
These material properties can be referred in either a CAD Graphic or an NLFE Body.
MotionView supports creating two types of materials:
| • | Linear Elastic |
| • | Hyper Elastic |
Isotropic, Orthotropic, and Anisotropic materials are supported within the Linear Elastic material type.
Default materials have properties that cannot be edited. You can add your own material by clicking on the Add button.
| 1. | Select the Elasticity Type of the material that is being added. Available options are: Linear Elastic and Hyper Elastic. |
| 2. | Click the Add button to bring up the Add a Material Property dialog. |
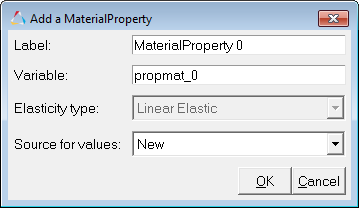
Add a Material Property dialog
The following options are available in the Add a Material Property dialog:
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
Label |
Specify a label for the material property. |
Variable |
Specify a variable name for the material property. |
Elasticity type |
The Elasticity type will either be Linear Elastic or Hyper Elastic based on the selection in Material Properties dialog when the Add button was clicked. |
Source for values |
Select either the material already available to copy the property values from, or select New. |
You can delete any material property that was added by selecting that material and clicking on the Delete button.
The following options are available in the Add a Material Property dialog:
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
Elasticity type |
Specify material elasticity type. Available options are: Linear Elastic and Hyper Elastic. |
Material |
Select the material for viewing/editing the properties. |
Type |
Specify the type of material. For Linear Elastic the available options are: Isotropic, Anisotropic, and Orthotropic. For Hyper Elastic the available options are: Neo-Hookean Incompressible, Neo-Hookean Compressible, Mooney-Rivlin, and Yeoh. |
Isotropic Material Properties |
|
Approach |
Works with a Beam type NLFE Body. If true, the material model considers the beam as an elastic line passing through the center line. The cross section and directional coupling effects on deformation is ignored. |
Modulus of elasticity (E) |
Specify the modulus of elasticity. |
Poisson ratio (v) |
Specify the Poisson's ratio. |
Density (ρ) |
Specify the material density. |
Elastic strain limit(εL) |
Specify a limit for the Elastic strain. For an NLFE Body, MotionSolve will provide warning whenever the strain in the body crosses this specified limit. |
Anisotropic Material Properties |
|
Stiffness [(1, 1), (1, 2),..] |
Specify the elements of the 6 x 6 stiffness matrix. |
Orthotropic Material Properties |
|
Modulus of elasticity (Ex) |
Specify the Young's modulus along X direction of the element. |
Modulus of elasticity (Ey) |
Specify the Young's modulus along Y direction of the element. |
Modulus of elasticity (Ez) |
Specify the Young's modulus along Z direction of the element. |
Shear modulus (Gxy) |
Specify the shear modulus in the XY plane of the element. |
Shear modulus (Gxz) |
Specify the shear modulus in the XZ plane of the element. |
Shear modulus (Gyz) |
Specify the shear modulus in the YZ plane of the element. |
Poisson ratio (vxy) |
Specify Poisson’s ratio for uni-axial loading in X direction. |
Poisson ratio (vxz) |
Specify Poisson’s ratio for uni-axial loading in Y direction. |
Poisson ratio (vyz) |
Specify Poisson’s ratio for uni-axial loading in Z direction. |
Density (ρ) |
Specify the material density. |
Elastic strain limit(εL) |
Specify the elastic strain limit. |
Hyper Elastic NeoHookean-InCompressible/Compressible |
|
Element shear modulus (µ) |
Specify the shear modulus. |
Poisson ratio (v) |
Specify the Poisson’s ratio. |
Density (ρ) |
Specify the material density. |
Elastic strain limit(εL) |
Specify the elastic strain limit. |
Hyper Elastic Mooney-Rivlin |
|
Element shear modulus (µ01) |
Specify the material constant. |
Element shear modulus (µ10) |
Specify the material constant. |
Poisson ratio (v) |
Specify the Poisson’s ratio. |
Density (ρ) |
Specify the material density. |
Elastic strain limit(εL) |
Specify the elastic strain limit. |
Hyper Elastic Yeoh |
|
Element shear modulus (c10) |
Specify the material constant. |
Element shear modulus (c20) |
Specify the material constant. |
Element shear modulus (c30) |
Specify the material constant. |
Poisson ratio (v) |
Specify the Poisson’s ratio. |
Density (ρ) |
Specify the material density. |
Elastic strain limit(εL) |
Specify the elastic strain limit. |
| Note | Changing the Units of the model will automatically change the material property values to the selected units. |
For Hyper Elastic materials, different constitutive material models are supported such as: Neo-Hookean (both compressible and incompressible), Mooney-Rivlin, and Yeoh models that are used to model a hyper elastic NLFE Body.
Hyper Elastic materials can undergo large deformations with a non-linear stress strain relationship.
The constitutive models for hyper elastic materials are characterized using the strain energy density function.
The following table lists the constitutive equations for various models:
Neo-Hookean |
|
|
Neo-Hookean Incompressible |
|
|
Mooney-Rivlin |
|
|
Yeoh |
|
|
The material constants for these models have to be derived through testing such as: uniaxial, bending, and shear tests.
For your convenience a set of materials are provided by default. The values of the properties provided are generic in nature, and might not be appropriate for the actual problem or material you intend to use with it. It is advised these materials be used with caution and that you obtain more accurate material properties.
|
Modulus of Elasticity |
Poisson Ratio (v) |
Density (ρ) |
Elastic strain limit (εL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Steel |
210000.0 |
0.3 |
7.86e-06 |
0.001 |
Aluminum |
70000.0 |
0.33 |
2.70e-06 |
0.001 |
Cast Iron |
120000.0 |
0.29 |
7.15e-06 |
0.001 |
Copper |
120000.0 |
0.34 |
8.96e-06 |
0.001 |
Brass |
106000.0 |
0.318 |
8.50e-06 |
0.001 |
Tin |
41600.0 |
0.33 |
5.77e-06 |
0.001 |
Bronze |
112000.0 |
0.324 |
8.40e-06 |
0.001 |
Nickel |
207000.0 |
0.31 |
8.88e-06 |
0.001 |
Titanium |
116000.0 |
0.34 |
4.50e-06 |
0.001 |
Zinc |
96500.0 |
0.33 |
7.1e-06 |
0.001 |
Belt Rubber |
500.0 |
0.42 |
1.50e-06 |
0.1 |
Source: www.matweb.com
Wood |
Property |
Value |
Modulus of Elasticity (Ex) (N/mm2) |
5200.0 |
|
Modulus of Elasticity (Ey) (N/mm2) |
78.0 |
|
Modulus of Elasticity (Ez) (N/mm2) |
239.0 |
|
Shear Modulus (Gxy) (N/mm2) |
192.4 |
|
Shear Modulus (Gxz) (N/mm2) |
280.8 |
|
Shear Modulus (Gyz) (N/mm2) |
26.0 |
|
Poisson Ratio ( |
0.488 |
|
Poisson Ratio ( |
0.229 |
|
Poisson Ratio ( |
0.231 |
|
Density ( |
4e-07 |
|
Elastic strain limit (εL) |
0.001 |
Source: Properties calculated for wood - Balsam popular based on table 5-1 to 5-3,
David E. Kretschmann, Mechanical properties of wood, Chapter 5
Type |
Property |
Value |
|---|---|---|
Neo-Hookean |
Shear Modulus ( |
0.3974 |
Poissons Ratio ( |
0.48 |
|
Density ( |
1.1e-06 |
|
Elastic strain limit (εL) |
2.0 |
|
Mooney-Rivlin |
Shear Modulus ( |
0.1615 |
Shear Modulus ( |
0.2856 |
|
Poissons Ratio ( |
0.48 |
|
Density ( |
1.1e-06 |
|
Elastic strain limit (εL) |
2.0 |
|
Yeoh |
Shear Modulus ( |
0.379 |
Shear Modulus ( |
0.0232 |
|
Shear Modulus ( |
-0.0003 |
|
Poissons Ratio ( |
0.48 |
|
Density ( |
1.1e-06 |
|
Elastic strain limit (εL) |
2.0 |
Source: : Analysis of Rubber Elastic Behaviour and Its Influence on
Modal Properties by Gabriel Anghelache and Raluca Moisescu,
University Politehnica of Bucharest
See Also
*MaterialProperty() (MDL Statement)