Multiple Input File Format |

|

|

|

|
|
Multiple Input File Format |

|

|

|

|
The multiple input format setup was the first to be introduced in RADIOSS Multi-Domain technique. Each subdomain is built as a separate complete RADIOSS model, using its own complete input files. The coupling between the RADIOSS Engine computations is ensured by the rad2rad program based on the connections between domains defined in each RADIOSS model.
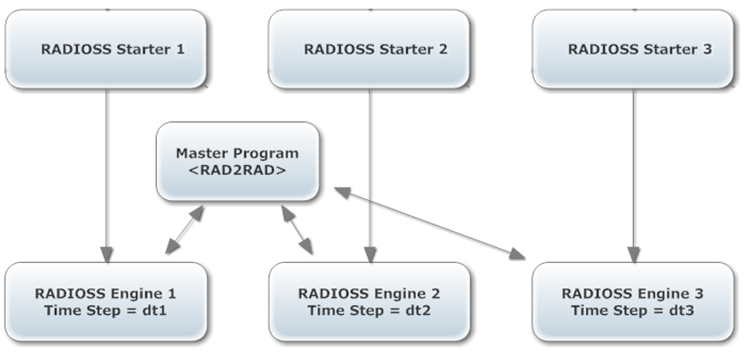
A connection (or link) between 2 domains is always defined by 2 groups of nodes relating to the two corresponding meshes to be connected to each other and the type of this connection. Below is a list of available types of connections in RAD2RAD.
It may be used to link shell element meshes through Lagrange multipliers. The meshes may be compatible or incompatible and the interfaces may be open or closed.
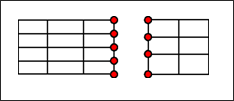
|
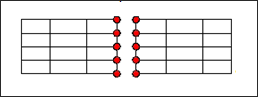
This type of link is very similar to Type 1; but it is adapted to beam/shell connection.
|
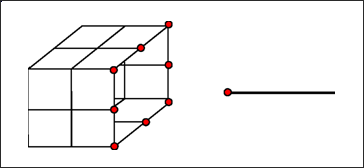
In the case of compatible meshes, the connection between domains can be reduced to simple node to node relations.
This method is strictly equivalent to Type 1 for compatible meshes; but consumes less CPU time, as no matrix assembly and no inversion have to be performed. Furthermore, in this case, since only nodal data is needed, it can be used to connect any type of nodes (attached to any type of elements).
|
It is also possible to compute contact between domains using the artificial skin method. The contacts are not computed by RAD2RAD, but inside one of the two domains called master domain. Therefore, the part of the slave domain concerned by the contact must be duplicated in the master domain with a void material having same density and Young’s modulus. The contact is then treated normally by RADIOSS inside the master domain and a node-to-node specific connection type 5 (similar to connection type 4) must be used to connect the nodes of the artificial skin and the corresponding nodes of the slave domain.
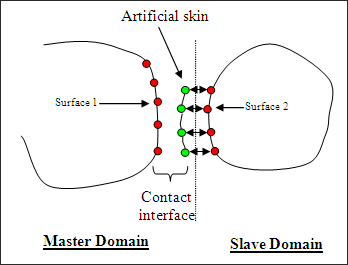
In the Multi-Domain master input file, the definition of connection type 5 is similar to other connections; except that the nodes of the master domain (nodes of the artificial skin) must be declared first:
/LINK/TYPE5
Master_Domain Link_Id1
Slave_Domain Link_Id2
The following RADIOSS contact interfaces are compatible with Multi-Domain:
| • | /INTER/TYPE24, if (surf_ID1 > 0, surf_ID2 > 0) or (surf_ID1 > 0, surf_ID2 = 0). Not if (grnd_IDs > 0, surf_ID1 = 0, surf_ID2 > 0). |
Mass and nodal stiffness are transferred by RAD2RAD connection type 5 from the slave domain to the artificial skin. Therefore, modifications of mass and nodal time step may be observed in the master domain at the beginning of the computation. |
In the Multi-Domain master input file, the definition of connection type 5 is similar to other connections; except that the nodes of the master domain (that is nodes of the artificial skin) must be declared first:
/LINK/TYPE5
Master_Domain Link_Id1
Slave_Domain Link_Id2
If kinematic constraints are applied on the part of the slave domain that is duplicated in the master domain, they must be duplicated as well.
| • | In the case of a rigid body duplication, the master node must be specified in the RAD2RAD connection type 5. |
| • | In the case of interface type 2 duplication, an additional flag /TIED must be specified in the RAD2RAD input file. |
|
Definition of connections (or links) between domains:
/EXTERN/LINK/Link_ID
title
gr_ID
Where, gr_ID is a nodal group identifier defining frontier nodes with other domain(s) and Link_ID is a link identifier.
The number of external links in a RADIOSS model is not limited. The only restriction is that different links should not contain common nodes. Each link defines a distinct interface between current model and the external world.
One Engine input file is required for each domain. In order to activate the coupling, all the Engine files must contain the following directive:
RAD2RAD Input File
The RAD2RAD input file is a text file defining some additional information required by the RAD2RAD program. The names of the domains to connect and the connections between domains must be specified in the RAD2RAD input file. For each connection the identifier of the links that are connected and the used connection types must be specified. Some Multi-Domain specific parameters also have to be entered.
|
There are two ways to launch a Multi-Domain computation, manually and through a script.
To manually launch a Multi-Domain computation, use the command line to browse to the working directory that containing the input files of the individual domains (_0000.rad and _0001.rad) and the Multi-Domain master input file (input.dat).
| • | Launch Starter for each domain in a terminal using the command: |
In UNIX: <install_dir>/hwsolvers/bin/linux64/s_version -i “filename”
In Windows: <install_dir>\hwsolvers\bin\win64\s_version -i “filename”
| • | Then launch RAD2RAD in a terminal using the command: |
In UNIX: <install_dir>/hwsolvers/bin/linux64/r2r_version input.dat
In Windows: <install_dir>\hwsolvers\bin\win64\r2r_version input.dat
RAD2RAD will then wait for RADIOSS connections from the individual domains.
| • | Launch Engine for the individual domains in separate terminals, as follows: |
In UNIX: <install_dir>/hwsolvers/bin/linux64/e_version -i “filename”
In Windows: <install_dir>\hwsolvers\bin\win64\e_version -i “filename”
All the RADIOSS processes will then connect automatically to RAD2RAD.
By Script
An easier way to launch a Multi-Domain computation is to use a script.
| • | Launch Starter for each domain the same way as described above |
| • | Add a script called "run_SMP" or "run_SPMD" in your working directory |
| • | In the script, change name of the input files, location of executables (MPI, RAD2RAD and RADIOSS Engine) and the number of processors, if necessary. |
| • | Run the script in a terminal |
./s_<version> < PART1_0000.rad ./s_<version> < PART2_0000.rad
./e_<version> < PART1_0001.rad > out_1 & ./e_<version> < PART2_0001.rad > out_2 & ./r2r_<version> input.dat
E:\Rad2rad\s_<version>.exe -i PART1_0000.rad E:\Rad2rad\s_<version>.exe -i PART2_0000.rad
set KMP_STACKSIZE=64M start /B E:\Rad2rad\e_<version>.exe -i PART1_0001.rad > out1 start /B E:\Rad2rad\e_<version>.exe -i PART2_0001.rad > out2 start /B E:\Rad2rad\r2r_<version>.exe input.dat
./s_<version>.exe < PART1_0000.rad; ./s_<version>.exe < PART2_0000.rad;
./e_<version>.exe < PART1_0001.rad > out1& ./e_<version>.exe < PART2_0001.rad > out2& ./r2r_<version>.exe data4.dat; |
./s_<version> < PART1_0000.rad ./s_<version> < PART2_0000.rad
/opt/hpmpi/bin/mpirun -np 4 ./e_<version> < PART1_0001.rad > out_1 & /opt/hpmpi/bin/mpirun -np 4 ./e_<version> < PART2_0001.rad > out_2 & ../exec/r2r_<version>_impi data4.dat
E:\Rad2rad\s_<version>.exe -i PART1_0000.rad -n 4 E:\Rad2rad\s_<version>.exe -i PART2_0000.rad -n 4
set KMP_STACKSIZE=64M start /B mpiexec -n 4 E:\Rad2rad\e_<version>.exe -i PART1_0001.rad > out1 start /B mpiexec -n 4 E:\Rad2rad\e_<version>.exe -i PART2_0001.rad > out2 start /B E:\Rad2rad\r2r_<version>.exe input.dat
./s_<version>.exe < PART1_0000.rad; ./s_<version>.exe < PART2_0000.rad;
mpiexec -n 4 ./e_<version>.exe < PART1_0001.rad > out1& mpiexec -n 4 ./e_<version>.exe < PART2_0001.rad > out2& ./r2r_<version>.exe data4.dat; |
The RADIOSS domains are treated alternately; which means that only one RADIOSS process is running at a time. The full CPU resource is automatically allocated by the RAD2RAD to the running Engine process and the other processes are put in a no CPU consuming waiting mode. It means that all the same available CPU resources must be allocated to each domain during its computation.
If the sizes of the Multi-Domain interfaces are big, the time spent in RAD2RAD for computing the coupling forces can be long. It is now possible to reduce this time by splitting the task of computing the coupling among several processors. Contrary to single input file setup, for the multiple input file setup only SMP parallelization of the RAD2RAD is available. The number of processors that can be used must be less than the number of cores available on the hardware node where RAD2RAD is launched. For example, a good value is 6 for a machine with 8 cores. The number of threads for the RAD2RAD can be specified using “-nt” in the command line like for the Engines or directly in the RAD2RAD input file using the keyword /PROC/nthread.
|
When using Multi-Domains and SPMD Engine executables, the followings MPI environment variables should be used in order to improve the performances:
| • | HP-MPI: MPI_FLAGS set to “y0” |
| • | Open-MPI: OMPI_MCA_mpi_yield_when_idle set to 1 |
| • | Intel-MPI: Default settings can be used |
| • | RADIOSS: Separate output files are generated by each RADIOSS process. |
| • | RAD2RAD: A specific output file named “rad2rad.out” is generated by RAD2RAD. |
| • | Each sub-domain is constructed as a complete. Separate RADIOSS model, using its own complete input files. |
| • | The data transfers between RADIOSS processes and master program use the pipe system method of communication. All RADIOSS Engines and the RAD2RAD must be started on the same hardware node. |
| • | Kinematic conditions on common nodes between domains are compatible only with connection type 5. |
| • | The RAD2RAD program is not parallelized for multiple input files setup. This may lead to reduced performance in Multi-Domain computations with large subdomains running on a large number of CPU's. |
| • | Currently, the Multi-Domain calculus is not automatically executed by the master program. All RADIOSS Starters must have been executed before the RAD2RAD program is launched. Although, batch execution is possible, RAD2RAD and all RADIOSS Engine processes must be launched independently and in parallel, on the single hardware node. |
| • | For each RADIOSS domain, the number of links is limited to 15 and the number of CPU's is limited to 128. |
Model RAD2RAD input file$=============================================================== $ RAD2RAD R8 INPUT FILE : $=============================================================== $ 1. PARTS DEFINITION $=============================================================== /DOMAIN/PART1 1 2 3 /DOMAIN/PART2 4 5 /DOMAIN/PART3 9 $=============================================================== $ 2. INTERFACES DEFINITION $=============================================================== /LINK/TYPE1 PART1 2 PART2 5 /LINK/TYPE1 PART1 1 PART2 4 /LINK/TYPE5 PART3 9 PART1 3 $=============================================================== $3 OPTIONS $=============================================================== /MLTPS/ON 0.1 0.1 /MESHL/MORFIN /RADIUS/1e-7 /END $=============================================================== |