Screw Joint |

|

|

|

|
|
Screw Joint |

|

|

|

|
This section describes the Screw joint entity of MotionView and shows the various usage, creation, and editing methods.
A Screw joint is a five degree-of-freedom kinematic pair used in mechanisms. Screw joints imposes a relation between the rotation of one body (Body 1) about an axis to the translation of the other body (Body 2) along an axis. The pitch of the joint completes this relation. One full rotation of Body 1 translates Body 2 by a distance equal to the 'pitch'.
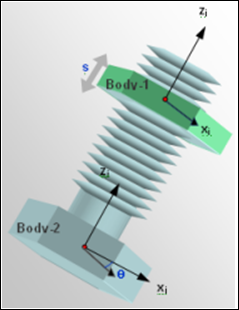
Screw joint construction
Screw joints are commonly used in applications, such as:
| • | Bolt and nut constraints |
| • | Rack and pinion steering |
| • | Any application where rotational motion needs to be converted to translation (or vice versa) |
The Screw joint is represented using Markers when exported to an MBD Solver. The representation can be visualized as shown in the figure below:
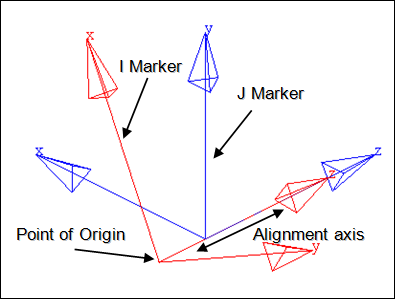
Screw joint marker representation
The bodies that are constrained by the Screw joint are represented using two markers: Marker I and Marker J. Marker I belongs to Body 1 and Marker J belongs to Body 2. The constraints and displacement are applied on the Marker I with respect to the Marker J. While defining the joint, the markers can either have coincident origins or they can be non-coincident. The alignment axis of the Screw joint is represented by the Z axis of both I and J markers. Marker I is constrained to translate along and rotate about the Z axis of Marker J by the magnitude decided by the 'pitch' of the joint.
The topological information required to define an Screw joint is shown in the figure below:
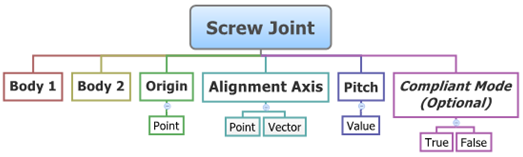
The data members of the Screw joint can be classified into the following members:
An Screw joint needs the following:
| • | Body 1 and Body 2 - Specify two Bodies between which the joint is to be created. |
| • | Origin - Specify Point, which defines the location of the joint. |
| • | Alignment Axis - Orientation of the joint specified using a Point or Vector. |
| • | Pitch - Specify the pitch value of the joint (see the Properties section below). |
| • | Compliant Mode (Optional) - If the Allow Compliance option is selected while adding the joint to a model, the joint's compliance state can be toggled between Compliant and Non-Compliant. |
The joint can be modeled as a Single entity or as a Pair entity.
To properly complete the definition of a screw joint, you must specify the Pitch. This is identical to the 'pitch' in a physical screw. One complete rotation of one body forces the other body connected by the joint to translate by a distance equal to the 'pitch'.
To learn how to add a Screw joint to a model, please see the Joints topic.
Joints Panel (Screw Joint) – Connectivity Tab - Single Entity
Joints Panel (Screw Joint) – Connectivity Tab - Pair Entity
Joints Panel (Screw Joint) – Properties Tab - Single Entity
Note - The same steps as shown above can also be used to define Pair Screw Joint entities. When defining a Pair Screw Joint use pair entities for Body 1, Body 2, Origin, etc. |
The Project Browser will filter the entities and display only the Joints in the model.
The corresponding panel is automatically displayed.
Joints panel - Connectivity tab - joint type drop-down menu |
The model containing the Screw Joint can be saved in MDL format from MotionView and exported in the MotionSolve XML format.
The Screw Joint can be of the following types:
These four types of entities can be added to the model using MDL Statements shown below:
To learn how to create a complete model using MDL Statements please refer to tutorial MV-1060: Introduction to MDL. |
The Screw joint when exported to the MotionSolve XML format is defined as a Constraint_Joint statement. Syntax: <Constraint_Joint id = "integer" label = "Name of Joint" type = "JOINT TYPE" i_marker_id = "integer" j_marker_id = "integer" pitch = "real" /> In the case of the Screw joint the model statement will be as shown below: <Constraint_Joint id = "301001" label = "Screw Joint" type = "SCREW" i_marker_id = "30103050" j_marker_id = "30101050" pitch = "10." /> In the above XML Model statement the i_marker_id and j_marker_id represent the I and J markers of the Joint which belong to Body 1 and Body 2 respectively. To understand the complete syntax of the Constraint_Joint XML model statement, please refer to the MotionSolve Reference Guide Page for Constraint_Joint. |
In MotionView, Tcl can be used to add any MDL entities to the model. There are two Tcl commands that can be used to add an entity:
Syntax: mdlmodel_handle InterpretEntity new_handle keyword varname label Example: mdlmodel_handle InterpretEntity joint_scr_handle ScrewJoint j_scr "\"Screw Joint\"" b_1 B_Ground p_ori "POINT" p_axis "ALLOW_COMPLIANCE"; |
Syntax: mdlmodel_handle InterpretSet keyword tokens Example: mdlmodel_handle InterpretSet Set j_scr.pitch "10" |
The InterpretEntity command is used to add entities to the model and the InterpretSet command is used to set the entity properties. So in the case of the Screw Joint, the property that can be set is the Pitch. Extended definitions for InterpretEntity and InterpretSet can be found in the HyperWorks Desktop Reference Guide.
Note - When using the InterpretEntity and InterpretSet commands, it is important to also use the Evaluate command in order for the changes to take effect immediately.
To learn how to create a complete model using Tcl commands, please refer to tutorial MV-1040: Model Building Using Tcl.
Example Model
The example file below shows a Screw joint connecting two bodies:
*BeginMDL( the_model, "Model", "12.0.110.40" ) *StandardInclude(FILE) *Point( p_0, "Point 0" ) *PointPair( p_1, "Point 1" ) *Body( b_0, "Body 0", p_0, , , , ) *BodyPair( b_1, "Body 1", p_1, , , , ) //Example for a Screw Joint - Single *ScrewJoint( j_Screwjsingle, "Screw Joint Single", b_0, B_Ground, p_0, POINT, p_1.r ) //Example for a Screw Joint - Pair *ScrewJointPair( j_Screwjpair, "Screw Joint Pair", b_1, B_Ground, p_1, VECTOR, V_Global_Y ) *SetPoint( p_1, LEFT, , -100 ) //Example for Set *Set( j_Screwjpair.l.pitch, 10 ) *Set( j_Screwjpair.r.pitch, 10 ) *EndMDL() |
See Also:
*ScrewJoint (MDL Model Statement)
*ScrewJointPair (MDL Model Statement)
*Set (MDL Model Statement)
Constraint_Joint (XML Command)
InterpretEntity (Tcl Command)
InterpretSet (Tcl Command)