Surface Interaction: Friction Tab |

|

|

|

|
|
Surface Interaction: Friction Tab |

|

|

|

|
The Friction tab allows you to create *FRICTION cards with corresponding parameters and data lines. The supported friction types (mutually exclusive parameters) are: Default (Coulomb), Elastic slip, Slip tolerance, Lagrange multiplier, and Rough. Depending on the template loaded and friction type selected, the window layout changes to show only the relevant options for defining other parameters and data items. Other supported optional parameters are: Exponential decay, Test data, Anisotropic, Taumax, and Dependencies. See the Abaqus documentation for detailed descriptions of these parameters.
|
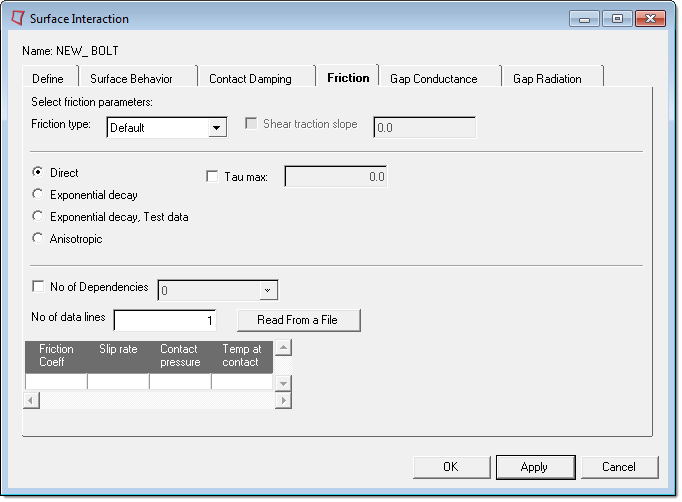
For all friction types (except Rough), there are four options to define the friction coefficient:
Direct |
This is the default method for defining the friction coefficient. Selecting this option means that the Exponential decay and Anisotropic parameters will not be written in the input file. The No of Dependencies check box and corresponding entry box should be used to define the Dependencies parameter. There is a table available for defining the corresponding data lines. The available data items are: Friction coefficient, Slip rate, Contact pressure, Average temperature at the contact point, and average field variable values. The column numbers in the table will change based on the setting for No of Dependencies. The row numbers can be defined at the No of data lines entry box. Click Set to update the table to reflect the specified number of rows. To enter values in the table, click on a cell to make it active and write down the values from keyboard. The table works like a regular spread sheet. You can also read comma delimited data from a text file by clicking Read From a File. This button opens a file browser. Select the file and click Open to export the comma delimited data. The row number will be set to the number of data lines found in the file. |
Anisotropic |
This option allows you to define the data lines for the Anisotropic parameter. The No of Dependencies check box and corresponding entry box should be used to define the Dependencies parameter. There is a table available for defining the corresponding data lines. The available data items are: Friction coefficient1 (first slip direction), Friction coefficient2 (second slip direction), Slip rate, Contact pressure, Average temperature at the contact point, and average field variable values. The column numbers in the table will change based on the setting for No of Dependencies. The row numbers can be defined at the No of data lines entry box. Click Set to update the table to reflect the specified number of rows. To enter values in the table, click on a cell to make it active and write down the values from keyboard. The table functions like a regular spread sheet. You can also read comma delimited data from a text file by clicking Read From a File. This button opens a file browser. Select the file and click Open to export the comma delimited data. The row number will be set to the number of data lines found in the file. |
Exponential decay |
This option allows you to define the data lines for the Exponential decay parameter. The available data items are: Static friction coefficient, Kinetic friction coefficient, and decay coefficient. |
Exponential decay, test data |
This option allows you to define the data lines for the Exponential decay, test data parameter. The available data items are: Friction coefficient at point 1 (first data line), Friction coefficient at point 2 (second data line), Slip rate at point 2 (second data line) and Kinematic friction coefficient (optional third data line). |
Note:
| • | Right-click in the table to display a pull-down menu containing copy, cut and paste options. Comma delimited data can be copied/cut into or pasted from the clipboard using these options. Hot keys, for example, CTRL-C, CTRL-X and CTRL-V on PC, can also be used. |
| • | Left-click in a cell to activate the cell. Click in an active cell to move the insertion cursor to the character nearest the mouse. |
| • | The SHIFT and CTRL keys can be used with a left mouse click to select multiple items in a table. |
| • | Press CTRL and the left or right arrow key to move the cursor within the active cell. Use the left, right, up and down arrows to change the active cell |
| • | Press Backspace to delete the character before the insertion cursor in the active cell. If multiple cells are selected, Backspace deletes all selected cells. |
| • | Press Delete to delete the character after the insertion cursor in the active cell. If multiple cells are selected, Delete deletes all selected cells. |
| • | Table columns can be resized by positioning the cursor along a column border, pressing the left or right mouse button, and dragging the border to a new position. |