MATX44 |

|

|

|

|
|
MATX44 |

|

|

|

|
Bulk Data Entry
MATX44 – Material Property Extension for Cowper-Symonds Elastic-plastic Material for Geometric Nonlinear Analysis
Description
Defines additional material properties for Cowper-Symonds elastic-plastic material for geometric nonlinear analysis.
Format
(1) |
(2) |
(3) |
(4) |
(5) |
(6) |
(7) |
(8) |
(9) |
(10) |
MATX44 |
MID |
A |
B |
N |
ICH |
SIGMAX |
C |
P |
|
|
ICC |
FSMOOTH |
FCUT |
EPSMAX |
EPST1 |
EPST2 |
|
|
|
|
Field |
Contents |
MID |
Material ID of the associated MAT1. No default (Integer > 0) |
A |
Plasticity yield stress. (Real > 0) |
B |
Plasticity hardening parameter. (Real > 0) |
N |
Plasticity hardening exponent. Default = 1.0 (Real) |
ICH |
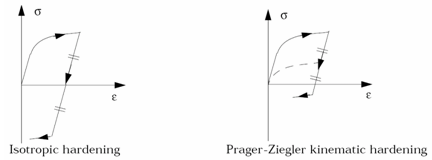
Hardening coefficient. 0.0: The hardening is a full isotropic model. Default = 0.0 (Real > 0) |
SIGMAX |
Maximum plastic stress σmax0 Default = 1030 (Real > 0) |
C |
Strain rate coefficient. Default = 0.0 (Real) |
P |
Strain rate exponent. Default = 1.0 (Real) |
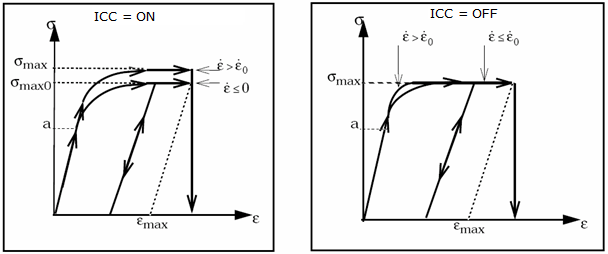
ICC |
Strain rate dependency of σmax flag. See comment 5. Default = ON (ON or OFF) |
FSMOOTH |
Strain rate smoothing flag. Default = OFF (ON or OFF) |
FCUT |
Cutoff frequency for strain rate filtering. Default = 1030 (Real > 0) |
EPSMAX |
Failure plastic strain. Default = 1030 (Real > 0) |
EPST1 |
Tensile rupture strain 1. Default = 1030 (Real > 0) |
EPST2 |
Tensile rupture strain 2. Default = 2.0 * 1030 (Real > 0) |
| 1. | The material identification number must be that of an existing MAT1 bulk data entry. Only one MATXi material extension can be associated with a particular MAT1. |
| 2. | MATX44 is only applied in geometric nonlinear analysis subcases which are defined by ANALYSIS = EXPDYN. It is ignored for all other subcases. |
| 3. | The Cowper-Symonds models an elastic-plastic material, only for solids and shells. The basic principle is the same as the standard Johnson-Cook model; the only difference between the two lies in the expression for strain rate effect on flow stress |
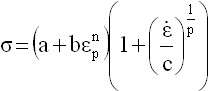
with εp being plastic strain, and ![]() being the strain rate.
being the strain rate.
| 4. | Hardening is defined by ICH. |
| 5. | ICC controls the strain rate effect. |

| 6. | No strain rate effects are considered in rod elements. |
| 7. | Strain rate filtering is used to smooth strain rates. The input FCUT is available only for shell and solid elements. |
| 8. | When the plastic strain reaches EPSMAX, the element is deleted. |
| 9. | If the first principal strain ε1 reaches εt1 = EPST1, the stress σ is reduced by: |
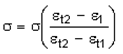
with εt2 = EPST2.
| 10. | If the first principal strain ε1 reaches εt2 = EPST2, the stress is reduced to 0 (but the element is not deleted). |
| 11. | If the first principal strain ε1 reaches εf = EPSF, the element is deleted. |
| 12. | This card is represented as an extension to a MAT1 material in HyperMesh. |
See Also: