PCNTX24 |

|

|

|

|
|
PCNTX24 |

|

|

|

|
Bulk Data Entry
PCNTX24 – Extended CONTACT Property type 24 for Geometric Nonlinear Analysis
Description
Defines properties type 24 of a CONTACT interface for geometric nonlinear analysis.
Format
(1) |
(2) |
(3) |
(4) |
(5) |
(6) |
(7) |
(8) |
(9) |
(10) |
PCNTX24 |
PID |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ISTF |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
GAPMAXs |
GAPMAXm |
|
|
|
STMIN |
STMAX |
IGAP0 |
IPEN0 |
IPENMAX |
IPENMIN |
|
|
|
|
STFAC |
FRIC |
|
TSTART |
TEND |
|
|
|
|
|
IBC |
|
|
INACTI |
VISS |
|
|
|
|
|
IFRIC |
IFILT |
FFAC |
|
SENSID |
|
|
|
|
|
FRICDAT |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
C5 |
C6 |
|
|
|
Field |
Contents |
PID |
Property identification number of the corresponding PCONT entry. No default (Integer > 0) |
ISTF |
Stiffness definition flag (See comment 5). Default as defined by CONTPRM (Integer = 0, …, 5) 0 - The stiffness is computed according to the master side characteristics. |
GAPMAXs |
Slave maximum gaps. (Real) |
GAPMAXm |
Master maximum gaps. (Real) |
STMIN |
Minimum stiffness (Only with ISTF > 1). Default as defined by CONTPRM (Real > 0) |
STMAX |
Maximum stiffness (Only with ISTF > 1). Default as defined by CONTPRM (Real > 0) |
IGAP0 |
Gap modification flag for slave shell nodes on the free edges. (Integer) 0 - No change 1 - Set gap to zero for the slave shell nodes |
IPEN0 |
Initial penetration detection flag (Integer) 0 - default method. Excludes the initial auto-impacts in the same part (shell and solid elements only). IPEN0 = 1 takes into account the initial auto-impacts in the same part, but in some complex situations, wrong initial penetrations might be given. 1 - method 1 (including auto-impact in each part) |
IPENMAX |
Maximum initial penetration: Penetration higher than this value will not be taken into account. (Real) |
IPENMIN |
Minimum initial penetration: Penetration higher than this value will be taken into account. (Real) |
STFAC |
Interface stiffness scale factor. Default as defined by CONTPRM (Real > 0) |
FRIC |
Coulomb friction. Default as defined by CONTPRM (Real > 0) |
TSTART |
Start time Default = 0.0 (Real > 0) |
TEND |
Time for temporary deactivation. Default = 1030 (Real > 0) |
IBC |
Flag for deactivation of boundary conditions at impact applied to the slave grid set. Default as defined by CONTPRM (Character = X, Y, Z, XY, XZ, YZ, or XYZ) |
INACTI |
Handling of initial penetrations flag. Default as defined by CONTPRM (Integer = 0, 1, -1, or 5) 0 - only tiny initial penetrations (1.0e-08) will be taken into account. Ignores the initial penetrations, but the contacts are not deleted, new contact will be well detected once the penetrations are disappeared gap0 = gap - P0, where P0 is the initial penetration |
VISS |
Critical damping coefficient on interface stiffness. Default as defined by CONTPRM (Real > 0) |
IFRIC |
Friction formulation flag (See comment 8). Default as defined by CONTPRM (Character = COUL, GEN, DARM, or REN) COUL - Static Coulomb friction law. |
IFILT |
Friction filtering flag (See comment 9). Default as defined by CONTPRM (Character = NO, SIMP, PER, or CUTF) NO - No filter is used. |
FFAC |
Friction filtering factor. Default as defined by CONTPRM |
SENSID |
Sensor identifier to Activate/Deactivate the interface (See comment 12) No default (Integer) If a sensor identifier is defined, the activation/deactivation of interface is based on the sensor and not on Tstart or Tstop. |
FRICDAT |
Indicates that additional information for IFRIC will follow. Only available when IFRIC = GEN, DARM or REN. |
C1, C2, C3, C4, C5, C6 |
Coefficients to define variable friction coefficient in IFRIC = GEN, DARM, or REN. Default as defined by CONTPRM (Real > 0) |
| 1. | The property identification number must be that of an existing PCONT bulk data entry. Only one PCNTX24 property extension can be associated with a particular PCONT. |
| 2. | PCNTX24 is only supported for geometric nonlinear explicit dynamic analysis subcase defined by ANALYSIS = EXPDYN. It is ignored for all other subcases. |
| 3. | If FRIC is not explicitly defined on the PCONTX/PCNTX# entries, the MU1 value on the CONTACT or PCONT entry is used for FRIC in the /INTER entries for Geometric Nonlinear Analysis. Otherwise, FRIC on PCONTX/PCNTX# overwrites the MU1 value on CONTACT/PCONT. |
| 4. | In implicit analysis, different contact formulations are used for contact where slave and master set do not overlap and where they overlap (self-contact). |
In the case of self-contact, the gap cannot be zero and a constant gap is used. For small initial gaps, the convergence will be more stable and faster if GAP is larger than the initial gap.
In implicit analysis, sometimes a stiffness with scaling factor reduction (for example, STFAC = 0.01) or reduction in impacted thickness (if rigid one) might reduce unbalanced forces and improve convergence, particularly in shell structures under bending where the effective stiffness is much lower than membrane stiffness; but it should be noted that too low of a value could also lead to divergence.
| 5. | If ISTF ≠ 1, the interface stiffness K is computed from the master segment stiffness Km and/or the slave segment stiffness Ks. |
The master stiffness is computed from Km = STFAC * B * S * S/V for solids, Km = 0.5 * STFAC * E * t for shells.
The slave stiffness is an equivalent nodal stiffness computed as Ks = STFAC * B * V-3 for solids, Ks = 0.5 * STFAC * E * t for shells.
In these equations, B is the Bulk Modulus, S is the segment area, and V is the volume of a solid. There is no limitation to the value of stiffness factor (but a value larger than 1.0 can reduce the initial time step).
The interface stiffness is K = max (STMIN, min (STMAX, K1)) with:
| • | ISTF = 0, K1 = Km |
| • | ISTF = 2, K1 = 0.5 * (Km + Ks) |
| • | ISTF = 3, K1 = max (Km, Ks) |
| • | ISTF = 4, K1 = min (Km, Ks) |
| • | ISTF = 5, K1 = Km * Ks / (Km + Ks) |
| 6. | The gap is computed automatically (similar with IGAP = VAR on PCNTX7) for each impact as gs + gm; |
with:
| • | gm - master element gap, with: |
gm = t/2, t: thickness of the master element for shell elements.
gm = 0 for solid elements.
| • | gs - slave node gap: |
gs = 0 if the slave node is not connected to any element or is only connected to solid or spring elements.
gs = t/2, t - largest thickness of the shell elements connected to the slave node.
gs = 1/2√S for truss and beam elements, with S being the cross section of the element.
gm and gs are limited separately by GAPMAXm and GAPMAXs before the gap computation.
| 7. | The coefficients C1 - C6 are used to define a variable friction coefficient |
| 8. | IFRIC defines the friction model. |
IFRIC = COUL – Coulomb friction with FT < FRIC * FN.
For IFRIC > 0 the friction coefficient is set by a function (![]() )
)
where, p is the pressure of the normal force on the master segment and V is the tangential velocity of the slave node.
The following formulations are available:
| • | IFRIC = GEN - Generalized viscous friction law |
![]() FRIC + C1 * p + C2 * V + C3 * p * v + C4 * p2 + C5 * v2
FRIC + C1 * p + C2 * V + C3 * p * v + C4 * p2 + C5 * v2
| • | IFRIC = DARM - Darmstad law |
![]() = C1 * e(C2V) * p2 + C3 * e(C4V) * p + C5 * e(C6V)
= C1 * e(C2V) * p2 + C3 * e(C4V) * p + C5 * e(C6V)
| • | IFRIC = REN - Renard law |
|
0 < V < C5 |
|
C5 < V < C6 |
|
C6 < V |
where:
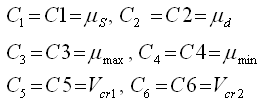
| • | The first critical velocity Vcr1 must not be 0 (C5 ≠ 0). It also must be lower than the second critical velocity Vcr2 (C5 < C6). |
| • | The static friction coefficient C1 and the dynamic friction coefficient C2, must be lower than or equal to the maximum friction C3 (C1 < C3 and C2 < C3). |
| • | The minimum friction coefficient C4, must be lower than or equal to the static friction coefficient C1 and the dynamic friction coefficient C2 (C4 < C1 and C4 < C2). |
| 9. | IFILT defines the method for computing the friction filtering coefficient. If IFILT ≠ NO, the tangential friction forces are smoothed using a filter: |
FT = α * F'T + (1 - α) * F'T-1
where,
FT is the tangential force
F'T is the tangential force at time t
F'T-1 is the tangential force at time t-1
α is the filtering coefficient
IFILT = SIMP – α = FFAC
IFILT = PER – α = 2![]() dt/FFAC, where dt/T = FFAC, T is the filtering period
dt/FFAC, where dt/T = FFAC, T is the filtering period
IFILT = CUTF – α = 2![]() * FFAC * dt, where FFAC is the cutting frequency
* FFAC * dt, where FFAC is the cutting frequency
| 10. | IFORM selects two types of contact friction penalty formulation. |
The viscous (total) formulation (IFORM = VISC) computes an adhesive force as:
Fadh = VISF * √(2KM) * VT
FT = min (µFN, Fadh)
The stiffness (incremental) formulation (IFORM = STIFF) computes an adhesive force as:
Fadh = FTold + ΔFT
ΔFT = K * VT * dt
FTnew = min (µFN, Fadh)
| 11. | When SENSID is defined for activation/deactivation of the interface, TSTART and TSTOP are not taken into account. |
| 12. | When the contact type is the symmetric surface to surface, the output normal contact forces in TH file are correctly calculated if the two surfaces are well separated. |
| 13. | For implicit test: Interface type24 is now only available with SMP. The default of ISTF will be set to 4. The default INACTI will be set to -1. |
| 14. | This card is represented as an extension to a PCONT property in HyperMesh. |
See Also: