TABLES1 |

|

|

|

|
|
TABLES1 |

|

|

|

|
TABLES1 – Material Property Tabular Function, Form 1
Defines a tabular function for use as stress-strain curve in elasto-plastic material properties MATS1, MATX33, MATX65, MATHF, as well as material curve in nonlinear material properties MATX36, MATX42, and MATX70. The TABLES1 entry can also be used to define the corresponding material curves on the MATHE Bulk Data Entry.
(1) |
(2) |
(3) |
(4) |
(5) |
(6) |
(7) |
(8) |
(9) |
(10) |
TABLES1 |
TID |
|
|
FLAT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
x1 |
y1 |
x2 |
y2 |
x3 |
y3 |
x4 |
y4 |
|
|
x5 |
y5 |
… |
… |
… |
… |
… |
… |
|
|
Field |
Contents |
TID |
Table identification number. No default (Integer > 0) |
FLAT |
Specifies the handling method for y-values outside the specified range of x-values in the table. = 0: If an x-value input is outside the range of x-values specified on the Table, the corresponding y-value look up is performed using linear extrapolation from the two start or two end points. = 1: If an x-value input is outside the range of x-values specified on the Table, the corresponding y-value is equal to the start or end points, respectively. Default = 0 (0 or 1) |
x#, y# |
Tabular values. No default (Real, or ENDT) |
Comments
| 1. | xi must be in either ascending or descending order, but not both. |
| 2. | Discontinuities between any two points except the two starting points or two end points. For example, in Figure 1 discontinuities are allowed only between points x2 through x7. Also, if y is evaluated at a discontinuity, the average value of y is used. In Figure 1, the value of y at x = x3 is y = (y3+y4)/2. |
| 3. | At least one continuation entry must be specified. |
| 4. | Any x, y pair may be ignored by placing 'SKIP' in either of the two fields used for that entry. |
| 5. | The end of the table is indicated by the existence of 'ENDT' in either of the two fields following the last entry. An error is detected if any continuations follow the entry containing the end-of-table flag 'ENDT'. |
| 6. | For FLAT=0 (default), TABLES1 uses the algorithm: |
![]()
Where, x is input to the table and y is returned. The table look-up is performed using interpolation within the table and linear extrapolation outside the table using the two starting or end points. See Figure 1. The algorithms used for interpolation or extrapolation is:
![]()
Where, xj and yj follow xi and yi.
For FLAT=1, the same algorithm as FLAT=0 is used, except that values outside the range are not extrapolated. The corresponding start or end point y-values are used for all y-values outside the range.
| 7. | For TABLES1 referenced by elasto-plastic material property MATS1, additional requirements apply. See the description of MATS1 for details. |
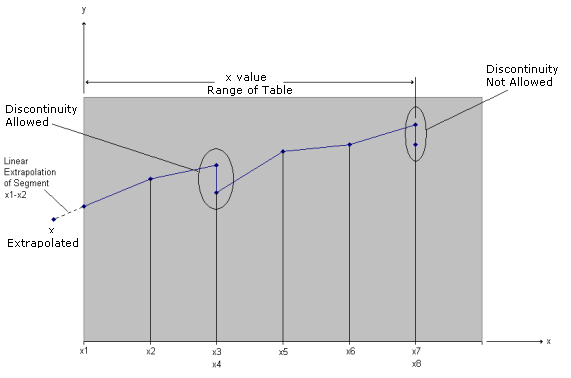
Figure 1. Example of Table Extrapolation and Discontinuity
| 8. | Linear extrapolation is not used for Fourier transform methods. The function is zero outside the range of the table. |
| 9. | For frequency-dependent loads, x# is measured in cycles per unit time. |
| 10. | Some warning or error messages are issued if table data in input incorrectly. However, since TABLES1 can serve different and distinct purposes, error checking is limited. |
See Also: