Field
|
Contents
|
SI Unit Example
|
prop_ID
|
Property identifier
(Integer, maximum 10 digits)
|
|
unit_ID
|
Optional unit identifier
(Integer, maximum 10 digits)
|
|
prop_title
|
Property title
(Character, maximum 100 characters)
|
|
Mass
|
Spring mass
(Real)
|
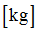
|
Inertia
|
Spring inertia
(Real)
|
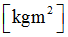
|
skew_ID
|
Skew system identifier
(Integer)
|
|
sens_ID
|
Sensor identifier
(Integer)
|
|
Isflag
|
Sensor flag
(Integer)
=0: See Comment 3
=1: See Comment 4
|
|
Ifail
|
Failure criteria
(Integer)
= 0: uni-directional criteria
= 1: multi-directional criteria
|
|
Ileng
|
Input per unit length flag
(Integer)
= 0: See Comment 2 and Comment 7
= 1: See Comment 8
|
|
Ifail2
|
Failure model flag
Default = 0 (Integer)
= 0: old displacement criteria
= 1: new displacement criteria
= 2: force criteria
= 3: internal energy criteria
|
|
K1
|
Stiffness for tension
(Real)
|
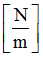
|
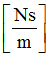
C1
|
Damping for tension
(Real)
|
|
A1
|
Coefficient for strain rate effect in tension (homogeneous to a force)
Default = 1.0 (Real)
|

|
B1
|
Logarithmic coefficient for strain rate effect in tension (homogeneous to a force)
(Real)
|

|
D1
|
Scale coefficients for elongation velocity
Default = 1.0 (Real)
|
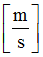
|
fct_ID11
|
Function identifier defining 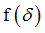
If H1 =4: Upper yield curve function identifier
(Integer)
= 0 for linear spring
|
|
H1
|
Hardening flag
(Integer)
= 0: Nonlinear elastic spring
= 1: Nonlinear elastic plastic spring
= 2: Nonlinear elasto-plastic spring with decoupled hardening in tension and compression
= 4: Nonlinear elastic plastic spring “kinematic” hardening
= 5: Nonlinear elasto-plastic spring with nonlinear unloading
= 6: Nonlinear elasto-plastic spring with isotropic hardening and nonlinear unloading
= 7: Nonlinear spring with elastic Hysteresis
|
|
fct_ID21
|
Function identifier defining 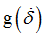
(Integer)
|
|
fct_ID31
|
Function used only for unloading
If H1=4: Function identifier defining lower yield curve
If H1=5: Function identifier defining residual displacement vs maximum displacement
(Integer)
|
|
fct_ID41
|
Function identifier defining 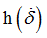
(Integer)
|
|
Hscale1
|
Coefficient for 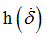 (homogeneous to a force) (homogeneous to a force)
Default = 1 (Real)
|
|
F1
|
Scale factor for 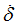 in function in function 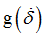
(Real)
|
|
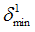
|
Negative failure limit
Default = -1030 (Real)
|
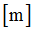
|
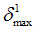
|
Positive failure limit
Default = 1030 (Real)
|
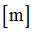
|
Ascale1
|
Abscissa scale factor for 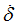 (fct_ID11 and fct_ID31) (fct_ID11 and fct_ID31)
(Real)
|
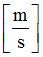
|
E1
|
Coefficient for strain rate in tension (homogeneous to a force)
(Real)
|

|
K3
|
Stiffness for torsion
(Real)
|
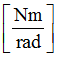
|
C3
|
Damping for torsion
(Real)
|
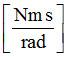
|
A3
|
Coefficient for strain rate effect in torsion (homogeneous to a moment)
Default = 1.0 (Real)
|

|
B3
|
Logarithmic coefficient for strain rate effect in torsion (homogeneous to a moment)
(Real)
|

|
D3
|
Scale coefficients for torsion velocity
Default = 1.0 (Real)
|

|
fct_ID13
|
Function identifier defining 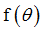
If H3=4: Function identifier defining upper yield curve
(Integer)
= 0: linear spring
|
|
H3
|
Hardening flag
(Integer)
= 0: Nonlinear elastic spring
= 1: Nonlinear elastic plastic spring
= 2: Nonlinear elasto-plastic spring with decoupled hardening in tension and compression
= 4: Nonlinear elastic plastic spring “kinematic” hardening
= 5: Nonlinear elasto-plastic spring with nonlinear unloading
= 6: Nonlinear elasto-plastic spring with isotropic hardening and nonlinear unloading
= 7: Nonlinear spring with elastic Hysteresis
|
|
fct_ID23
|
Function identifier defining 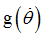
(Integer)
|
|
fct_ID33
|
Function used only for unloading
If H3=4: Function identifier defining lower yield curve
If H3=5: Function identifier defining residual displacement vs maximum displacement
(Integer)
|
|
fct_ID43
|
Function identifier defining 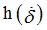
(Integer)
|
|
Hscale3
|
Coefficient for 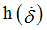 (homogeneous to a force) (homogeneous to a force)
Default = 1 (Real)
|
|
F3
|
Scale factor for 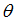 in function in function 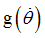
(Real)
|

|
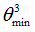
|
Negative failure limit
Default = -1030 (Real)
|

|
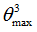
|
Positive failure limit
Default = 1030 (Real)
|

|
Ascale3
|
Abscissa scale factor for 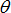 (fct_ID13 and fct_ID33) (fct_ID13 and fct_ID33)
(Real)
|

|
E3
|
Coefficient for strain rate effects in torsion (homogeneous to a moment)
(Real)
|

|
K2
|
Stiffness for shear
(Real)
|
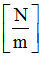
|
C2
|
Damping for shear
(Real)
|

|
A2
|
Coefficient for strain rate effect in shear (homogeneous to a force)
Default = 1.0 (Real)
|

|
B2
|
Logarithmic coefficient for strain rate effect in shear (homogeneous to a force)
Default = 1.0 (Real)
|

|
D2
|
Scale coefficients for shear velocity
Default = 1.0 (Real)
|
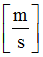
|
fct_ID12
|
Function identifier defining 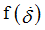
If H2=4: Function identifier defining upper yield curve
(Integer)
= 0: linear spring
|
|
H2
|
Hardening flag
(Integer)
= 0: Nonlinear elastic spring
= 1: Nonlinear elastic plastic spring
= 2: Nonlinear elasto-plastic spring with decoupled hardening in tension and compression
= 4: Nonlinear elastic plastic spring “kinematic” hardening
= 5: Nonlinear elasto-plastic spring with nonlinear unloading
= 6: Nonlinear elasto-plastic spring with isotropic hardening and nonlinear unloading
= 7: Nonlinear spring with elastic Hysteresis
|
|
fct_ID22
|
Function identifier defining 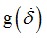
(Integer)
|
|
fct_ID32
|
Function used only for unloading
If H2=4: Function identifier defining lower yield curve
If H2=5: Function identifier defining residual displacement vs maximum displacement
(Integer)
|
|
fct_ID42
|
Function identifier defining 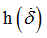
(Integer)
|
|
Hscale2
|
Coefficient for 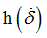 (homogeneous to a force) (homogeneous to a force)
Default = 1 (Real)
|
|
F2
|
Scale factor for 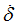 in function in function 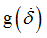
(Real)
|
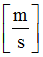
|
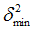
|
Negative failure limit
Default = -1030 (Real)
|
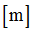
|
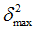
|
Positive failure limit
Default = 1030 (Real)
|
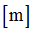
|
E2
|
Coefficient for strain rate effect in shear (homogeneous to a force)
(Real)
|

|
Ascale2
|
Abscissa scale factor for 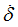 (fct_ID12 and fct_ID32) (fct_ID12 and fct_ID32)
(Real)
|
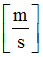
|
K4
|
Stiffness for bending
(Real)
|
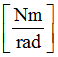
|
C4
|
Damping for bending
(Real)
|
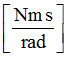
|
A4
|
Coefficient for strain rate effect in bending (homogeneous to a moment)
Default = 1.0 (Real)
|

|
B4
|
Logarithmic coefficient for strain rate effect in bending (homogeneous to a moment)
Default = 1.0 (Real)
|

|
D4
|
Scale coefficients for bending velocity
Default = 1.0 (Real)
|

|
fct_ID14
|
Function identifier defining 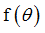
If H4=4: Function identifier defining upper yield curve
(Integer)
= 0: linear spring
|
|
H4
|
Hardening flag
(Integer)
= 0: Nonlinear elastic spring
= 1: Nonlinear elastic plastic spring
= 2: Nonlinear elasto-plastic spring with decoupled hardening in tension and compression
= 4: Nonlinear elastic plastic spring “kinematic” hardening
= 5: Nonlinear elasto-plastic spring with nonlinear unloading
= 6: Nonlinear elasto-plastic spring with isotropic hardening and nonlinear unloading
= 7: Nonlinear spring with elastic Hysteresis
|
|
fct_ID24
|
Function identifier defining 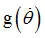
(Integer)
|
|
fct_ID34
|
Function used only for unloading
If H4=4: Function identifier defining lower yield curve
If H4=5: Function identifier defining residual displacement vs maximum displacement
(Integer)
|
|
fct_ID44
|
Function identifier defining 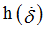
(Integer)
|
|
Hscale4
|
Coefficient for 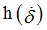 (homogeneous to a force) (homogeneous to a force)
Default = 1 (Real)
|
|
F4
|
Scale factor for 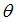 in function in function 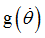
(Real)
|

|

|
Negative failure limit
Default = -1030 (Real)
|

|
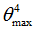
|
Positive failure limit
Default = 1030 (Real)
|

|
Ascale4
|
Abscissa scale factor for 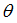 (fct_ID14 and fct_ID34) (fct_ID14 and fct_ID34)
(Real)
|

|
E4
|
Coefficient for strain rate effect in bending (homogeneous to a force)
(Real)
|

|
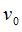
|
Reference translational velocity
Default = 1.0 (Real)
|
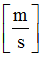
|
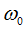
|
Reference rotational velocity
Default = 1.0 (Real)
|

|
c1
|
Relative velocity coefficient in translation X
Default = 0.0 (Real)
|
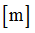
|
n1
|
Relative velocity exponent in translation X
Default = 0.0 (Real)
|
|
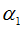
|
“Mult” factor in translation X
Default = 1.0 (Real)
|
|
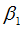
|
Exponent in translation X
Default = 2.0 (Real)
|
|
c2
|
Relative velocity coefficient in shear
Default = 0.0 (Real)
|
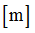
|
n2
|
Relative velocity exponent in shear
Default = 0.0 (Real)
|
|
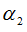
|
“Mult” factor in shear
Default = 1.0 (Real)
|
|
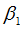
|
Exponent in shear
Default = 2.0 (Real)
|
|
c3
|
Relative velocity coefficient in torsion X
Default = 0.0 (Real)
|

|
n3
|
Relative velocity exponent in torsion X
Default = 0.0 (Real)
|
|
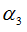
|
“Mult” factor in torsion X
Default = 1.0 (Real)
|
|
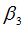
|
Exponent in torsion X
Default = 2.0 (Real)
|
|
c4
|
Relative velocity coefficient in bending
Default = 0.0 (Real)
|

|
n4
|
Relative velocity exponent in bending
Default = 0.0 (Real)
|
|
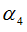
|
“Mult” factor in bending
Default = 1.0 (Real)
|
|
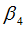
|
Exponent in bending
Default = 2.0 (Real)
|
|







